Fig. 1
Fig. 1
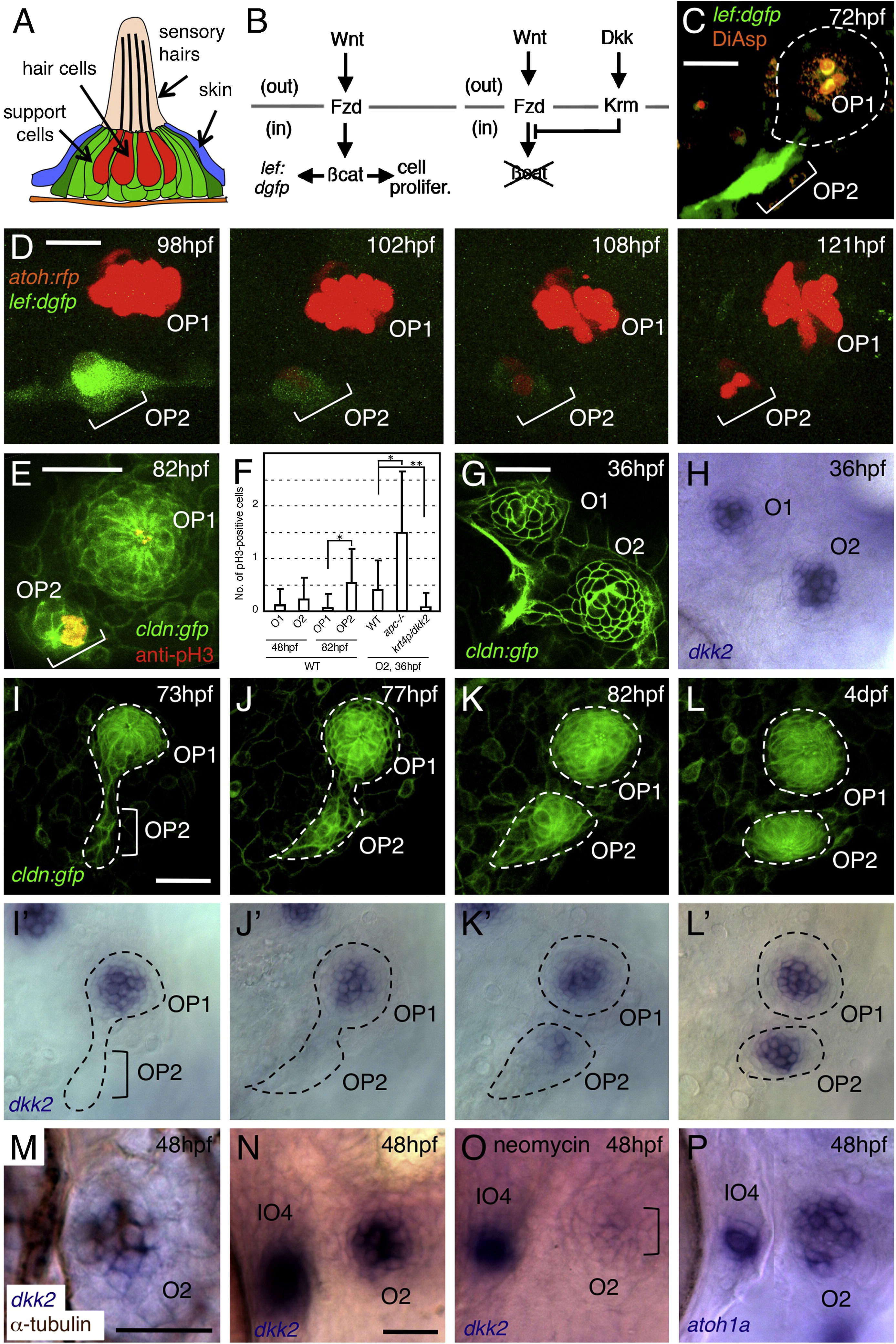
Wnt Signaling and Expression of dkk2 Are Associated with Neuromast Proliferation
(A) Schematic drawing of a neuromast in transverse view.
(B) Schematic representation of Wnt signaling through its receptor, Frizzled (Fzd), and of its inhibition by Dickkopf (Dkk) signaling through its receptor, Kremen (Krm). out, extracellular compartment; in, intracellular compartment.
(C) Wnt signaling is detectable only in budding cells (OP2), but not in mature neuromast (OP1), as revealed in a Wnt-responsive GFP reporter line.
(D) The expression of dGFP gradually subsides as hair cells (labeled with atoh:rfp) are formed in O2.
(E) Anti-phosphohistone H3 (pH3) labeling indicates dividing cells in budding neuromast (OP2), but not in mature neuromast (OP1).
(F) Number of pH3-positive cells per neuromast. Mean ± SEM is indicated. p < 0.001, p < 0.01 (t test).
(G and H) dkk2 mRNA is expressed by cells in the center of neuromasts O1 and O2.
(I–L2) Expression profile of dkk2 during neuromast budding. dkk2 mRNA expression coincides with neuromast maturation. The budding structures are outlined.
(M) dkk2 mRNA (blue) is present in hair cells (brown).
(N and O) dkk2 expression is reduced in O2 after ablation of hair cells but is not affected in immature neuromast IO4.
(P) atoh1a mRNA is present in O2 and IO4.
Scale bars represent 20 μm. See also Figure S1.