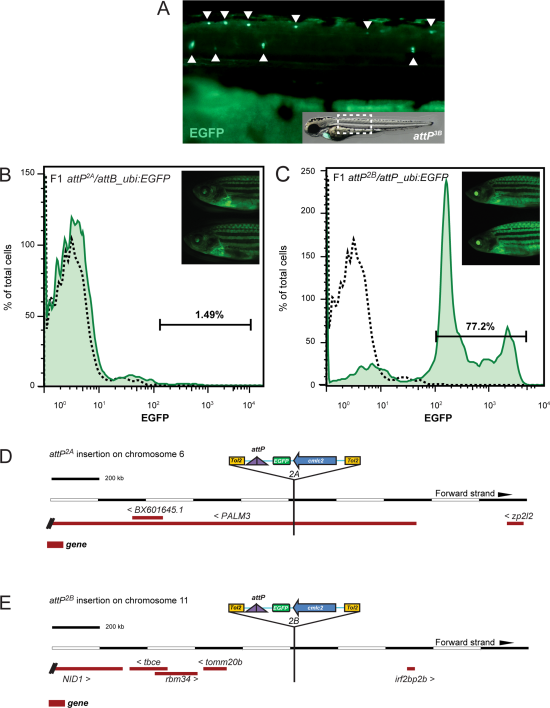
Fig. 4
Characterization of individual functional attP transgenic landing site lines. A: Example for enhancer trapping of an attP site transgene. Line attP3B shows prominent EGFP expression in spinal cord neurons and the lateral line, indicating integration of the attP landing site in the proximity of a neuronal enhancer. Arrowheads indicate EGFP-misexpressing neurons, white dotted box marks area of close up. B, C: Flow cytometry analysis for EGFP expression in whole kidney marrow (WKM) of adult F1 attP/attB_ubi:EGFP transgenics to assess stable ubi:EGFP expression in the hematopoietic lineages. Despite strong overall EGFP expression (inset), line attP2A shows no hematopoietic cells with EGFP (B), indicating transgene silencing in adult blood lineages. In contrast, line attP2B (C) shows faithful EGFP expression in all adult hematopoietic populations. Representative flow cytometry analysis of individual animals is shown, separated by forward scatter (FSC) and side scatter (SSC); dotted black line indicates EGFP results for uninjected attP, cmlc2:EGFP control. D,E: Integrations shown as based on Ensembl Genome Browser; Zv9 assembly, modified to show transgene orientation. The genomic integration locus of individual attP sites was identified by TAIL-PCR using arbitrary degenerated primers binding in the genomic region adjacent to the attP insert together with nested Tol2-specific primers reading out of the transgene cassette (see Experimental Procedures section for details). D: attP2AB maps to the first intron of the annotated gene PALM3 on chromosome 6, causing no obvious aberrant phenotype but resulting in silenced hematopoietic transgene expression. E: attP2B maps to an approximately 650-kb-spanning intergenic region on chromosome 11, suggestive of a neutral insertion locus.