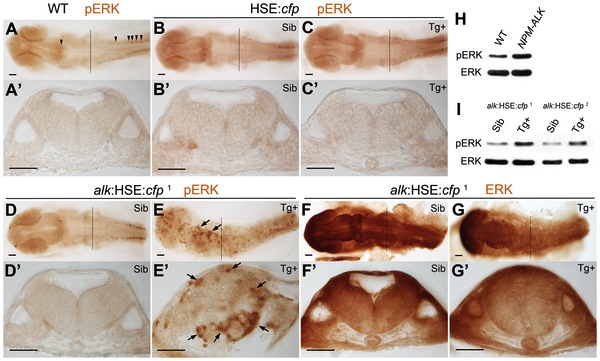
Fig. 3 MAPK signaling is activated upon alk overexpression.
(A,A′) phospho-ERK (pERK) immunostaining of a 24 hpf wild-type embryo without heat shock. Endogenous MAPK activation is evident in the caudal most hindbrain and spinal cord, but low in other parts of the CNS. (B,B′,C,C′) Both Sib (B,B′) and Tg+ embryos (C,C2) of the HSE:cfp control line were normal and no additional pERK was observed. (D,D2,E,E2) Ectopic pERK (arrows) was evident in Tg+ (E,E′) of the alk:HSE:cfp1 line compared to Sib (D,D′). (F,F2,G,G′) Total ERK was ubiquitously distributed in both Sib (F,F2) and Tg+ (G,G′) embryos of the alk:HSE:cfp1 line and showed no difference. (A2–G2) Transverse sections from embryos at r5 level as indicated by black lines in (A–G). Sib, transgenic negative siblings. Tg+, transgenic positive embryos. ERK, total ERK1/2. pERK, phosphorylated-ERK1/2. Scale bars: 50 µm. (H) Western blot analysis showing more pERK protein in NPM-ALK mRNA injected embryos than in WT at 11 hpf. Each lane represents protein content from five embryos of a 20–50 embryo pool. (I) Western blots showing increased pERK levels in Tg+ versus Sib embryos at 22 hpf in both alk:HSE:cfp lines. Each lane contains proteins equivalent to five embryos of a 20–50 embryo pool. Only dissected anterior parts of embryos were used to eliminate endogenous pERK originating from spinal cord and tail bud.