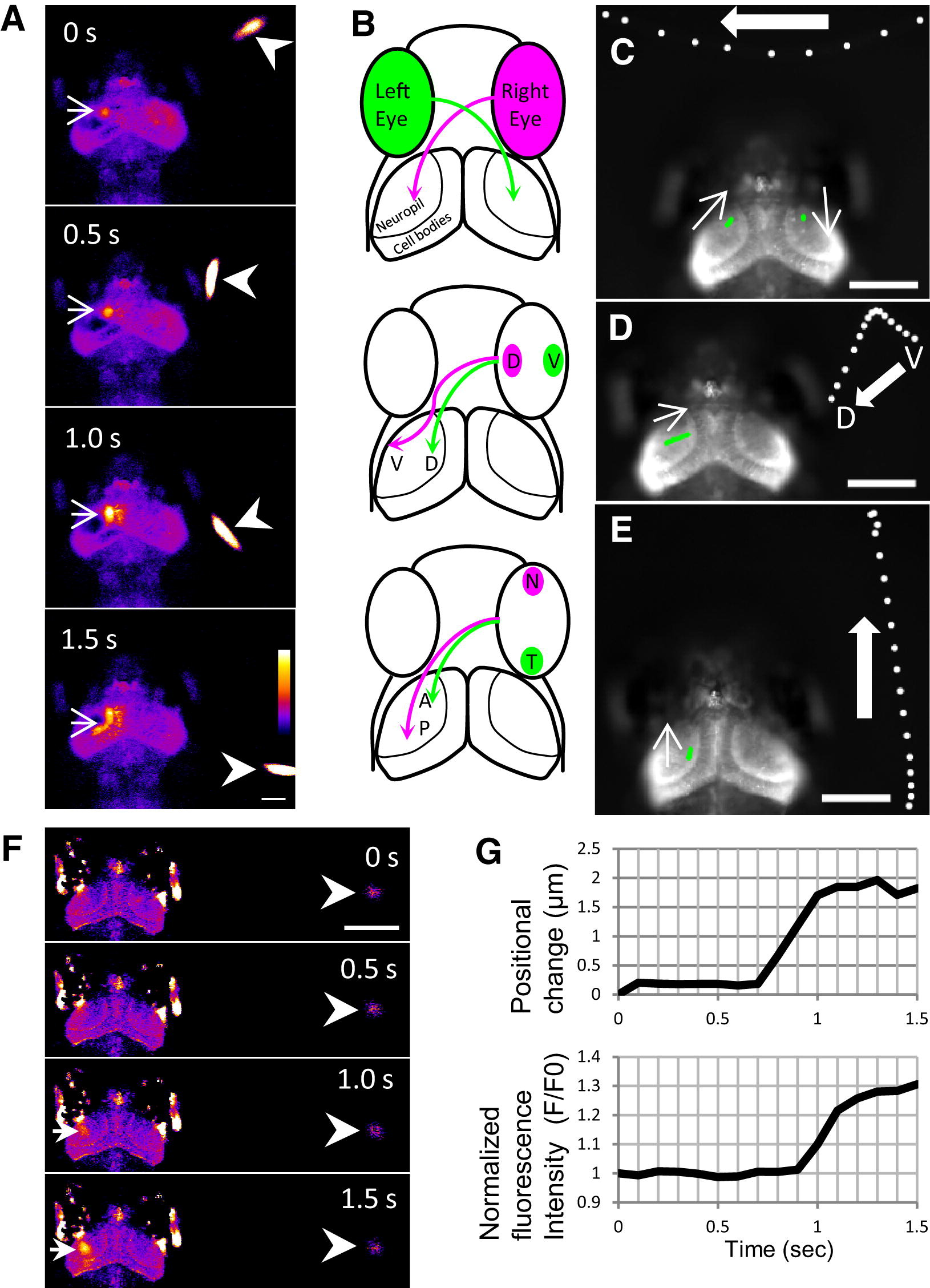
Fig. 3 Tectal Responses during Perception of a Swimming Paramecium(A) In response to a swimming paramecium (arrowheads), Ca2+ transients (arrows) were detected in the neuropil and cell bodies of the left tectum of a 7 dpf larva embedded in agarose (Movie S3). Ratio images were created and pseudocolored. Scale bar represents 100 μm.(B) Retinotopic projections of the retinal ganglion cell axons: D, dorsal; V, ventral; N, nasal; T, temporal; A, anterior; P, posterior.(C–E) Functional visuotopy (Movie S3). White spots indicate the positions of a paramecium, moving in the indicated directions. Green spots indicate the positions of Ca2+ signals in the neuropil. Scale bars represent 100 μm.(C) A paramecium moved from the right to left hemifield, and the Ca2+ signal moved from the left to right tectum.(D) A paramecium and Ca2+ signals moved from ventral to dorsal.E) A paramecium and Ca2+ signals moved from posterior to anterior.(F and G) Ca2+ signals in the tectum of a 7 dpf larva evoked by motion of a paramecium (Movie S4).(F) Ratio images of Ca2+ signals (arrows) detected when a paramecium (arrowheads) started to move. Scale bar represents 250 μm.(G) Graph plots of Ca2+ signals and positional changes of the paramecium. The paramecium started to move at 0.7 s (upper graph), and the fluorescence change was detectable after 0.9 s (lower graph).
Image
Figure Caption
Figure Data
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Curr. Biol.