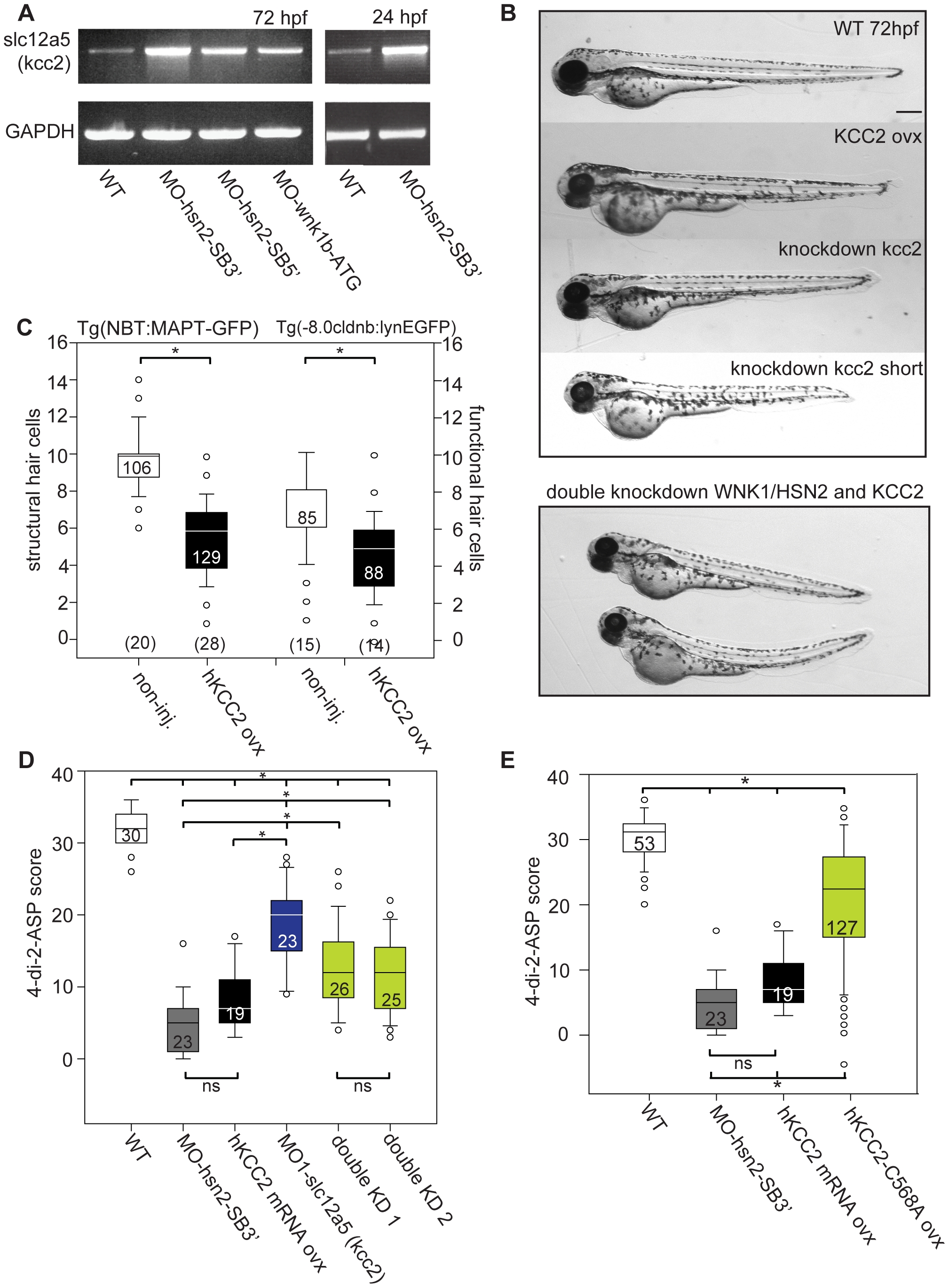
Fig. 4
KCC2 is overexpressed in WNK1/HSN2 knockdown embryos.
A) RT-PCR against slc12a5 (coding for kcc2) shows higher levels of RNA in WNK1/HSN2 knockdown embryos when compared with WT at 72hpf as well as at 24hpf. We overexpressed human KCC2 mRNA in WT embryos (morphology presented in (B)) to validate this result and were able to replicate the WNK1/HSN2 knockdown phenotype as assayed by (C) the number of structural and functional hair cells in PLL neuromasts and by (D) the 4-di-2-ASP score. We also validated this result by obtaining a partial rescue of the WNK1/HSN2 knockdown phenotype by knocking down kcc2 using MO1-slc12a5 in WNK1/HSN2 embryos (double knockdown-KD experiments). The embryos lacking kcc2 have morphological defects and a lower 4-di-2-ASP score (D) due to their smaller length (B), but double knockdown embryos, which are also morphologically abnormal and smaller in size have a significantly higher 4-di-2-ASP score (D) indicative of a partial rescue. For (C) The number of neuromasts counted per condition is indicated in the boxes and the total number of embryos obtained per condition is indicated in parenthesis at the bottom of the box plots. For (D), the total number of embryos is indicated in the boxes. (E) Overexpression of inactive mutant KCC2-C568A mimics hKCC2 overexpression and WNK1/HSN2 knockdown phenotype by producing PLL defects as assayed by 4-di-2-ASP vital dye staining. This indicates that WNK1/HSN2 interacts with KCC2 and regulates its transcription independent of the cotransporter′s activation. Neuromast scores were tabulated as previously done and presented as a box plot. The number of neuromasts counted per condition is indicated in the boxes. Scale bar: 100μm.