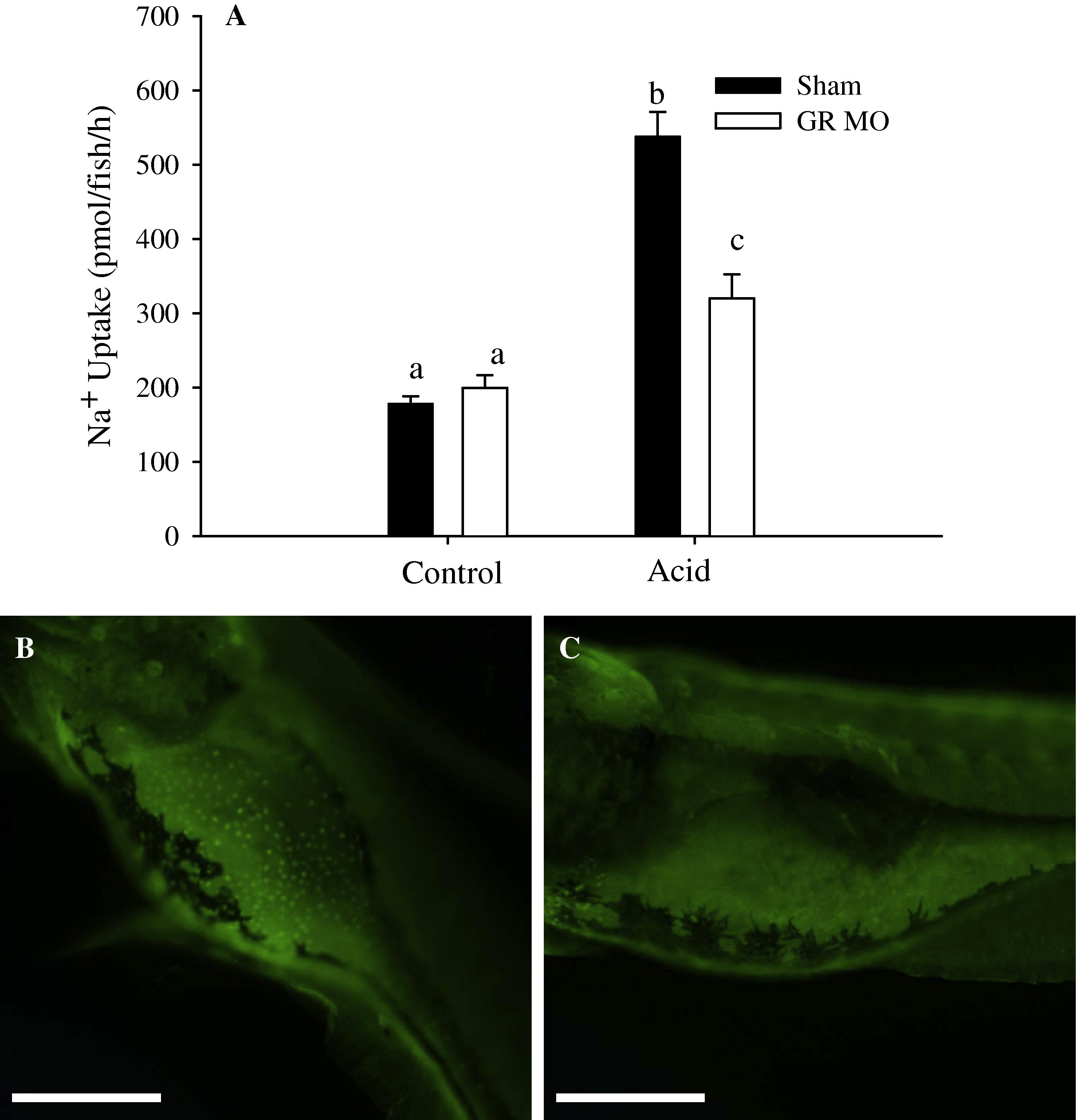
Fig. 4 The effects of exposure to acidic water on Na+ uptake in GR morphants. GR knockdown did not have any effect on Na+ uptake by zebrafish larvae maintained under normal pH (7) conditions (Fig. 4A, N = 6). However, while not eliminated entirely, the stimulation of Na+ uptake following 24-h exposure to acidic water was significantly attenuated in the GR morphants (Fig. 4A; N = 6). Data are presented as means ± SEM; different letters denote significant difference among treatment groups. The effectiveness of GR knockdown was confirmed by demonstrating via immunocytochemistry a marked reduction in the number of GR-positive cells on the yolk sac in the GR-MO’s (Fig. 4C) in comparison to the control MO’s (4C). Scale bars = 200 μm (4B and 4C).
Reprinted from Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology, 364(1-2), Kumai, Y., Nesan, D., Vijayan, M.M., and Perry, S.F., Cortisol regulates Na(+) uptake in zebrafish, Danio rerio, larvae via the glucocorticoid receptor, 113-125, Copyright (2012) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Mol. Cell. Endocrinol.