Fig. S4
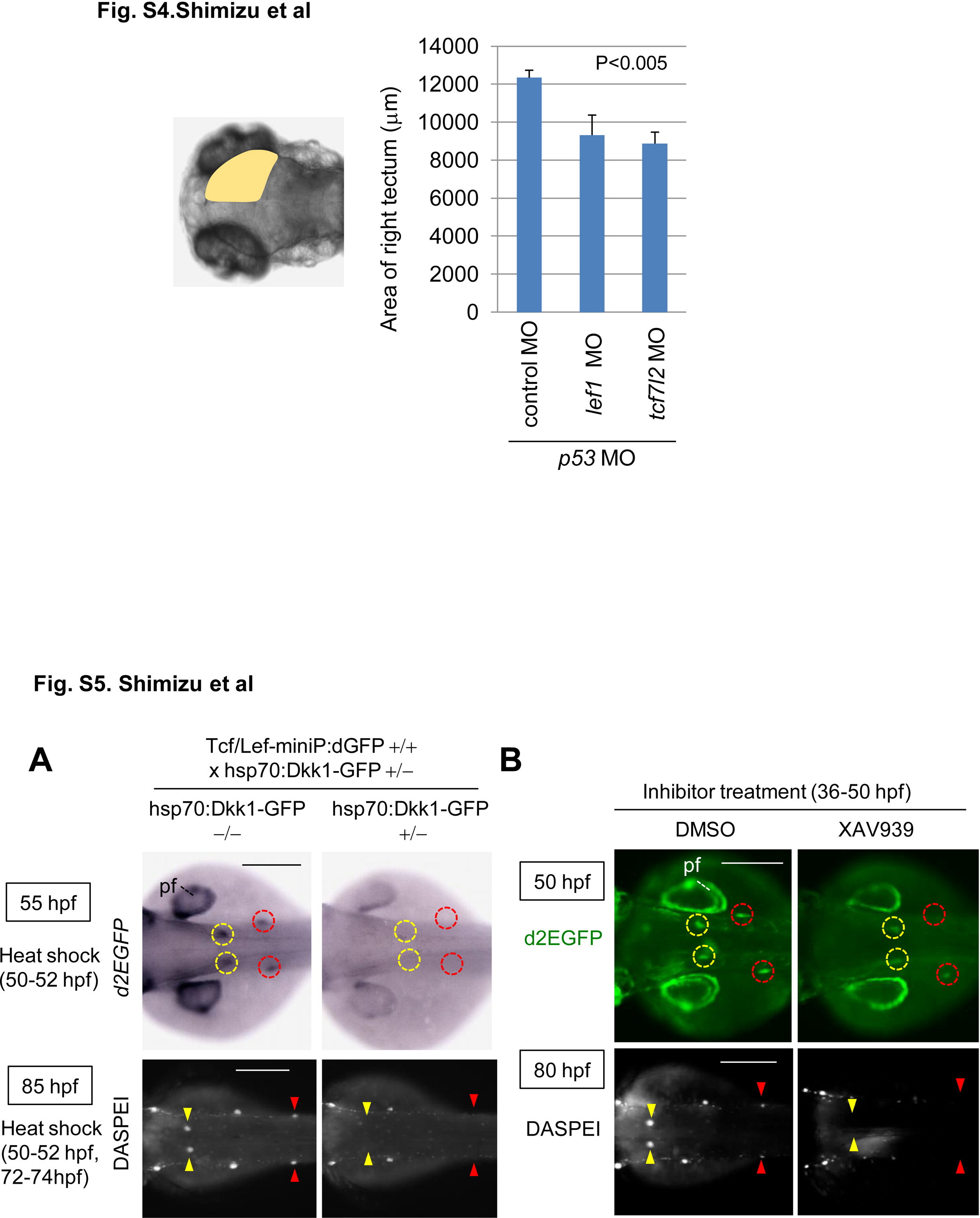
Knockdown of lef1 or tcf7l2 reduces the size of the midbrain tectum at 80 hpf. Graphs show the area of 80 hpf zebrafish embryos injected with control MO (n = 13), lef1 MO (n = 17), or tcf7l2 MO (n = 15) with p53 MO. The p value was calculated by Student′s t test. and Figure S5. Wnt/β-catenin signaling was required for dorsal and secondary pLL development. (A, B) Induction of Dkk1-GFP expression or XAV939 treatment blocked Tcf/Lef-miniP:dGFP reporter activity in the prim-D and prim-II and reduced the neuromast number. (A) hsp70:Dkk1-GFP-carrying Line-2 embryos were generated and classified using methods similar to those shown in Fig. 2A. Normal Line-2 embryos or hsp70:Dkk1-GFP-carrying Line-2 embryos were exposed to heat shock for 2 h at 37°C at 50 hpf. d2EGFP expression was detected by in situ hybridization 3 h after heat shock (top panels in A). Neuromasts were visualized by DASPEI staining 11 h after additional heat shock for 2h at 37°C at 72 hpf. Panels show trunk views of embryos, with the anterior side to the left. (B) Panels show trunk views of 50- (upper panels) and 80-hpf (lower panels) reporter fish embryos treated with DMSO or 10 μM XAV939 from 36 to 50 hpf, with the anterior side to the left. d2EGFP-expressing cells were visualized by fluorescence microscopy (lower panels). (A, B) DASPEI-stained cells were observed by fluorescence microscopy. prim-Ds and prim-IIs are surrounded with yellow and red circles, respectively. DASPEI-stained prim-D- and prim-II-derived neuromasts are indicated with yellow and red arrowheads, respectively. Note that Dkk1-GFP expression or XAV939 treatment also reduced d2EGFP expression in the pectoral fin fold (pf). Scale bar, 200 μm. and Knockdown of lef1 or tcf7l2 reduces the size of the midbrain tectum at 80 hpf. Graphs show the area of 80 hpf zebrafish embryos injected with control MO (n = 13), lef1 MO (n = 17), or tcf7l2 MO (n = 15) with p53 MO. The p value was calculated by Student′s t test. and Figure S5. Wnt/β-catenin signaling was required for dorsal and secondary pLL development. (A, B) Induction of Dkk1-GFP expression or XAV939 treatment blocked Tcf/Lef-miniP:dGFP reporter activity in the prim-D and prim-II and reduced the neuromast number. (A) hsp70:Dkk1-GFP-carrying Line-2 embryos were generated and classified using methods similar to those shown in Fig. 2A. Normal Line-2 embryos or hsp70:Dkk1-GFP-carrying Line-2 embryos were exposed to heat shock for 2 h at 37°C at 50 hpf. d2EGFP expression was detected by in situ hybridization 3 h after heat shock (top panels in A). Neuromasts were visualized by DASPEI staining 11 h after additional heat shock for 2h at 37°C at 72 hpf. Panels show trunk views of embryos, with the anterior side to the left. (B) Panels show trunk views of 50- (upper panels) and 80-hpf (lower panels) reporter fish embryos treated with DMSO or 10 μM XAV939 from 36 to 50 hpf, with the anterior side to the left. d2EGFP-expressing cells were visualized by fluorescence microscopy (lower panels). (A, B) DASPEI-stained cells were observed by fluorescence microscopy. prim-Ds and prim-IIs are surrounded with yellow and red circles, respectively. DASPEI-stained prim-D- and prim-II-derived neuromasts are indicated with yellow and red arrowheads, respectively. Note that Dkk1-GFP expression or XAV939 treatment also reduced d2EGFP expression in the pectoral fin fold (pf). Scale bar, 200 μm.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 370(1), Shimizu, N., Kawakami, K., and Ishitani, T., Visualization and exploration of Tcf/Lef function using a highly responsive Wnt/beta-catenin signaling-reporter transgenic zebrafish, 71-85, Copyright (2012) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.