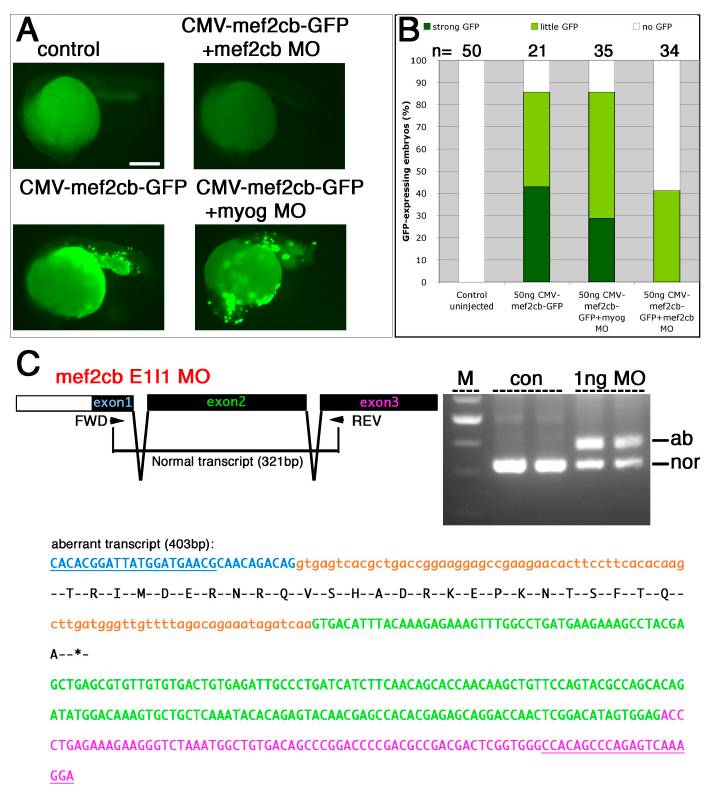
Fig. S3
Mef2cb morpholinos are specific and efficient in targeting translation and splicing of mef2cb.
A and B. mef2cb ATG MO specifically blocked translation of mef2cb-GFP mRNA. Representative embryos (A) and quantification (B) of mosaic GFP accumulation in 24 hpf embryos injected with pCMV:mef2cb-GFP, with or without MOs. Embryos injected with plasmid alone or with plasmid and control myog MO, have numerous cells with strong GFP. In contrast, embryos injected with plasmid and mef2cb ATG MO had little if any GFP expression. C. Schematic diagram of 5′UTR (white) and ORF (black) of Exons 1-3 in mef2cb mRNA and RT-PCR strategy used to detect spliced mRNAs in control and mef2cb E1I1 MO-injected embryos (top left). Gel showing RT-PCR of mRNA from 24 hpf uninjected control and mef2cb E1I1 MO-injected embryos (two independent samples each, top right). Morphant cDNA had strong reduction of the normal splice form (nor; 321 bp) and the appearance of a large aberrant band (ab; 403 bp). The aberrant transcript (bottom) results in a premature stop codon. Exon (upper case) and intron sequences (lower case) are coloured (exon1, blue; intron1, orange; exon2, green; exon3, purple). Primer sequences are underlined. Amino acid sequence of the aberrant CDS is shown below the nucleotide sequence leading to a stop codon in the first half of the MADS domain. Scale = 100 μm.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 369(2), Hinits, Y., Pan, L., Walker, C., Dowd, J., Moens, C.B., and Hughes, S.M., Zebrafish Mef2ca and Mef2cb are essential for both first and second heart field cardiomyocyte differentiation, 199-210, Copyright (2012) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.