Fig. S1
Related to Figure 1. The morphological and functional polarity of neuromast hair bundles is tuned to the A-P axis.
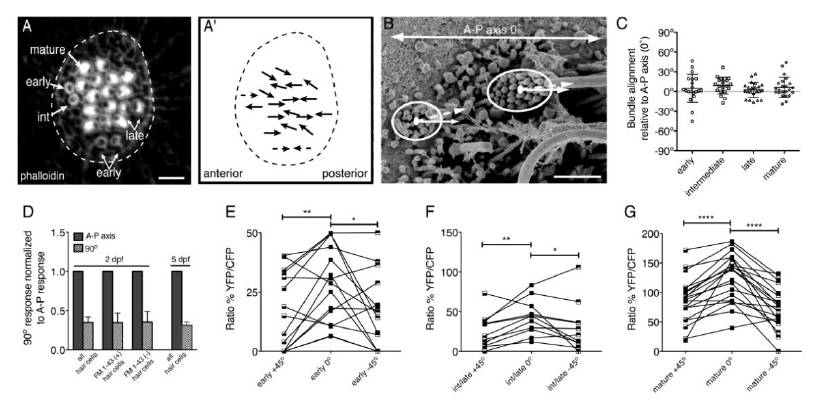
(A) A top down view of a neuromast stained with phalloidin to reveal bundle polarity at 5 dpf. (A′) Solid arrows indicate morphological polarity of each hair bundle in A. Dashed arrows indicate predicted hair-bundle polarity. (B) Method for scoring morphological hair-bundle polarity using SEM. An ellipse was drawn to encompass all stereocilia in each hair bundle. From the center of each ellipse a line was drawn bisecting the kinocilium (dashed line). The angle relative to the A-P axis (solid line) was then calculated. (C) Quantification of hair-bundle polarity using the technique described in (B) for each stage of hair-bundle development; n > 20 hair bundles scored for each stage. (D) In wildtype at 2 dpf, bundle deflection perpendicular to the A-P axis reduced responses similarly in both FM 1-43 labeled and unlabeled hair cells and compared to mature neuromasts at 5 dpf (n = 4 neuromasts per condition). (E, F and G) The calcium response of early, intermediate/late and mature hair bundles stimulated along the A-P axis (0°), and ± 45° off this axis either ventrally or dorsally. An unpaired Student’s t-test found no significant difference comparing any two stages in (C). When normalized to naïve response, a Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed rank test found no significant difference in the reduction between any two populations in (D). A paired Student’s t-test indicated that 45° off the A-P axis, there was a significant reduction in response at all stages in (E, F and G). Error bars in (C and D) represent s.e.m. * P< 0.05; ** P < 0.01; **** P < 0.0001. Scale bar is 5 μm in (A) and 1 μm in (B).
Reprinted from Developmental Cell, 23(2), Kindt, K.S., Finch, G., and Nicolson, T., Kinocilia mediate mechanosensitivity in developing zebrafish hair cells, 329-341, Copyright (2012) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Cell