Fig. S1
(related to Figure 2). Isl1 co-localizes with Ajuba and WTIP
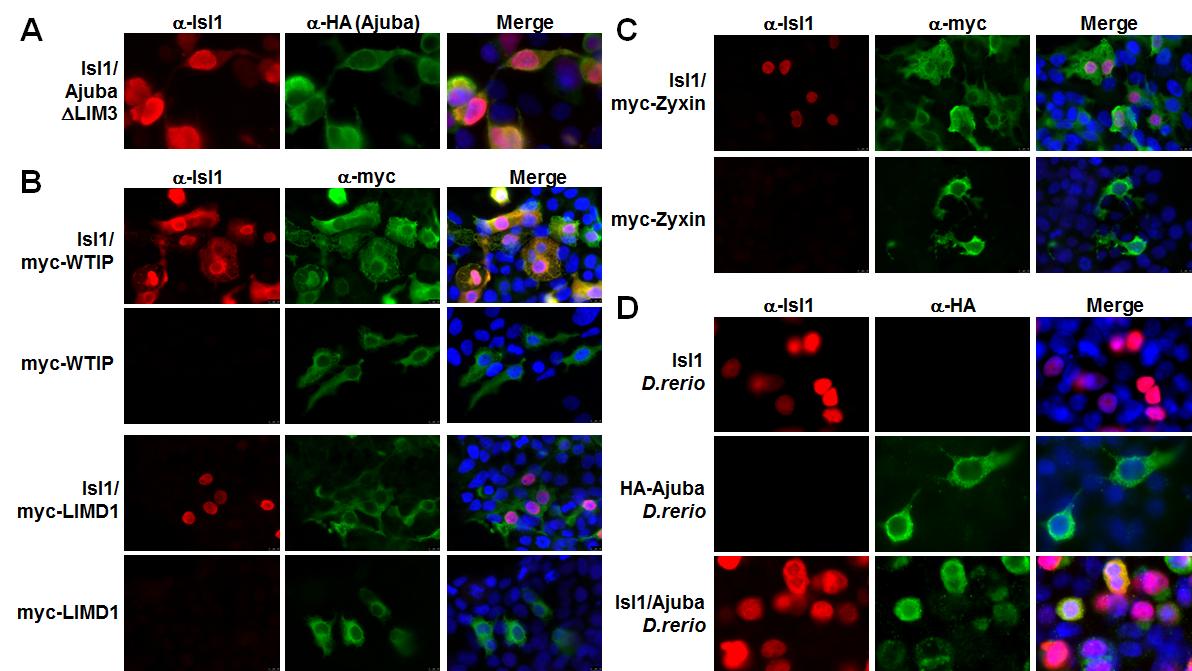
(A) Isl1 and FLAG-HA-tagged Ajuba lacking the LIM3 domain, which is not responsible for its interaction with Isl1, were transiently expressed in HEK 293T cells and immunofluorescent staining with anti-HA or anti-Isl1 antibodies was performed. The co-expression of Isl1 and the AjubaΔLIM3 protein affected the localization of both proteins: Isl1 was retained in the cytoplasm, and concomitantly, a significant amount of the Ajuba protein localized in the nucleus. (B) Subcellular localization of Isl1 and the members of the Ajuba protein family, WTIP and LIMD1, in HEK 293T cells. Myc-tagged WTIP, LIMD1 and Isl1 were transiently expressed, and immunofluorescence with anti-myc and anti-Isl1 antibodies was performed. Strong co-localization of WTIP with Isl1 was observed, but no co-localization was observed for LIMD1. (C) Subcellular localization of Isl1 and Zyxin in HEK 293T cells. Myc-tagged Zyxin and Isl1 were transiently expressed, and immunofluorescence with anti-myc or anti-Isl1 antibodies was performed. No co-localization was observed. (D) Subcellular localization of Isl1 and Ajuba from Danio rerio in HEK 293T cells. FLAG-HA-tagged Ajuba (D. rerio) and Isl1 (D. rerio) were transiently expressed, and immunofluorescence with anti-HA and anti-Isl1 antibodies was performed. Co-transfection of Ajuba and Isl-1 led to substantial co-localization.
Reprinted from Developmental Cell, 23(1), Witzel, H.R., Jungblut, B., Choe, C.P., Crump, J.G., Braun, T., and Dobreva, G., The LIM Protein Ajuba Restricts the Second Heart Field Progenitor Pool by Regulating Isl1 Activity, 58-70, Copyright (2012) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Cell