Fig. S4
(related to Figure 4). Chemokine signaling deficiency compromises proper lymphatic network formation
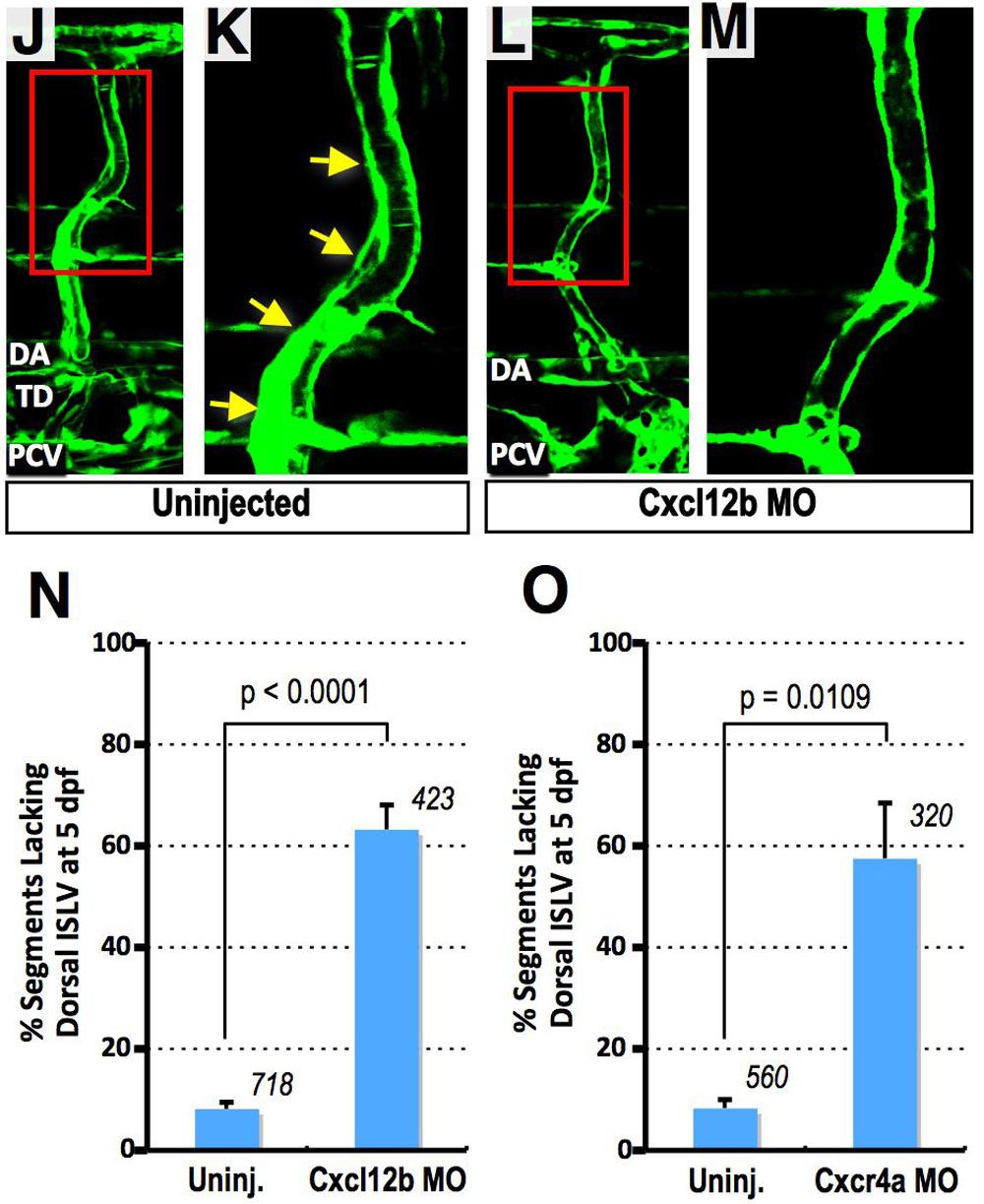
(A-F) Translation-blocking Cxcl12a MO (Cxcl12a MO2) results in defects of both PC and TD formation. (A and B) Confocal images of trunk vessels in 55 hpf Tg(fli-EGFP)y1 embryos that were either not injected (A), or injected with Cxcl12a MO2 (B). White arrows indicate PC. (C and D) Confocal images of trunk vessels in 5 dpf Tg(fli-EGFP)y1 embryos that were either not injected (C), or injected with Cxcl12a MO2 (D). Red, yellow arrows, and magenta arrowheads indicate DA, TD, and secondary sprouts migrating to the level of the HM, respectively. (E) Quantification of PC formation defects in 55 hpf Cxcl12a MO2-injected embryos (as shown in A and B). The total number of segments counted is shown above each bar. (F) Quantification of PC formation defects in 5 dpf Cxcl12a MO2- injected embryos (as shown in C and D). The total number of segments counted is shown above each bar. (G-I) Cxcl12a knockdown results in PC formation defects without affecting initiation and growth to the horizontal myoseptum of PCV-derived sprouts. (G) Confocal image of trunk vessels in 55 hpf Tg(fli-EGFP)y1 embryos injected with 15 ng Plcg MO. (H) Confocal image of trunk vessels in 55 hpf Tg(fli-EGFP)y1 embryos injected with 9 ng Cxcl12a MO + 15 ng Plcg MO. (I) Quantification of PC formation defect in 55 hpf MO-injected embryos (as shown in G and H). Values are the mean ± SEM. The total number of segments counted is shown above each bar. Secondary sprouts emerge from the PCV and grow to the level of the horizontal myoseptum (HM) in Plcg/Cxcr4a double MO-injected animals (H and I) but fail to form the PC (white arrows), as they do in animals injected with Plcg MO alone (G and I). (J-N) Dorsal migration of lymphatic endothelial cells from the PC is compromised in Cxcl12b-deficient embryos. (J and K) Confocal images of trunk vessels in un-injected 5 dpf Tg(fli-EGFP)y1 embryos, with magnified view of red box in J shown in K. Yellow arrows indicate an ISLV aligned along the dorsal part of an aISV. (L and M) Confocal images of trunk vessels in Cxcl12b MO-injected 5 dpf Tg(fli-EGFP)y1 embryos, with magnified view of red box in L shown in M. Note the absence of an ISLV aligned along the dorsal aISV. (N) Quantification of defects in alignment of ISLV along dorsal aISV in 5 dpf Cxcl12b MO-injected embryos (as shown in J-M). (O) Quantification of defects in alignment of ISLV along dorsal aISV in 5 dpf Cxcr4a MO-injected embryos. For N and O values are the mean ± SEM, and the total number of aISV examined for the presence of a co-aligned ISLV is shown above each bar.
Reprinted from Developmental Cell, 22(4), Cha, Y.R., Fujita, M., Butler, M., Isogai, S., Kochhan, E., Siekmann, A.F., and Weinstein, B.M., Chemokine Signaling Directs Trunk Lymphatic Network Formation along the Preexisting Blood Vasculature, 824-836, Copyright (2012) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Cell