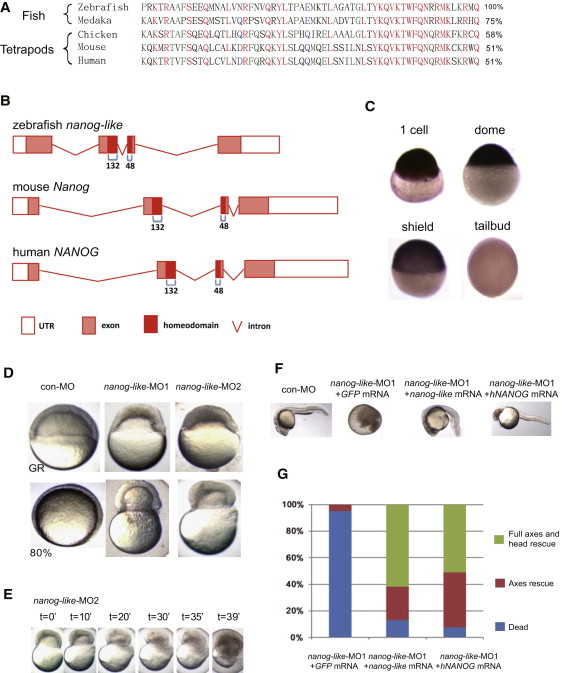
Fig. 1
Identification of the Zebrafish nanog-like Gene
(A) Alignment of the homeodomain sequence of fish and tetrapod Nanog proteins. The percentage similarity of each to zebrafish Nanog-like is shown at the right.
(B) Intron/exon structure of the zebrafish, mouse, and human Nanog genes. The 60-aa homeodomain is encoded by the last 132 bp of the second exon and the first 48 bp of the third exon in all three organisms.
(C) Whole-mount in situ hybridization of nanog-like identified high maternal (1-cell) and blastula (dome) expression, and rapidly diminishing expression during gastrulation (shield and tailbud stages).
(D) Blastomeres of nanog-like-knockdown embryos, injected with one of two distinct morpholinos targeting the translational start site, failed to thin at the germ ring stage and constricted to squeeze out the yolk cell by the 80% epiboly stage.
(E) Time-lapse microscopy of the nanog-like-MO2-injected embryo showing the yolk burst process.
(F) Rescue of the nanog-like-MO1-injected embryos by coinjection of 100 pg zebrafish nanog-like or human NANOG mRNA. Embryos shown are at 24 hpf.
(G) Statistics for the rescue of nanog-like-MO1-injected embryos by zebrafish nanog-like or human NANOG mRNA. A total of 100 GFP mRNA-injected, 115 nanog-like mRNA-injected, and 209 human NANOG mRNA-injected embryos were analyzed. Phenotype classes were counted at 24 hpf and are presented as a percentage of the whole.
Reprinted from Developmental Cell, 22(3), Xu, C., Fan, Z.P., Müller, P., Fogley, R., Dibiase, A., Trompouki, E., Unternaehrer, J., Xiong, F., Torregroza, I., Evans, T., Megason, S.G., Daley, G.Q., Schier, A.F., Young, R.A., and Zon, L.I., Nanog-like Regulates Endoderm Formation through the Mxtx2-Nodal Pathway, 625-238, Copyright (2012) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Cell