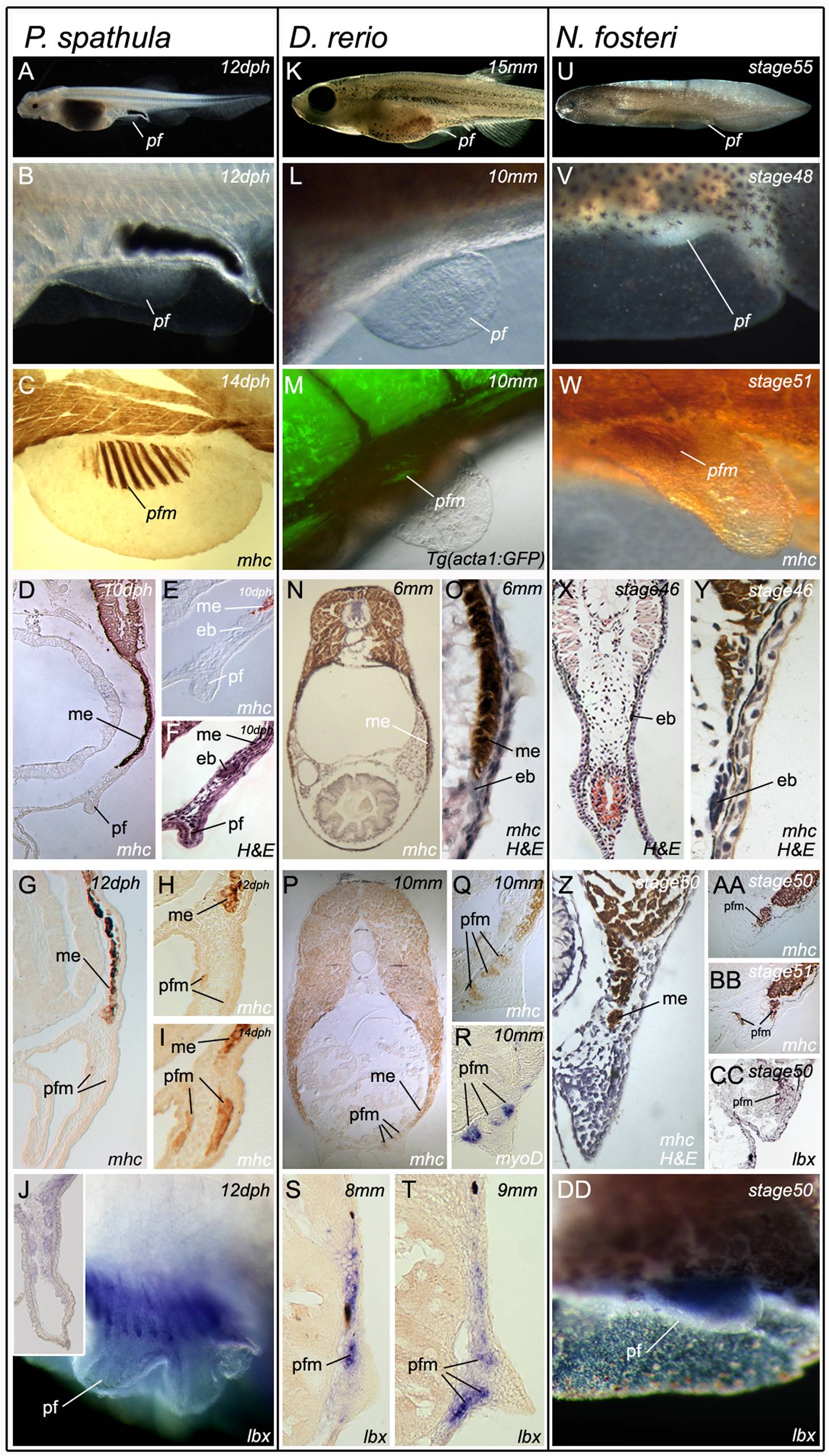
Fig. 4 Pelvic fin muscle formation in bony fish.
Pelvic fin muscle formation in P. spathula (A–J), D. rerio (K–T), and N. forsteri (U–DD). Larvae at stages when pelvic fin muscles form (A, K, and U). Developing pelvic fin bud (B, L, and V). Muscle fibres in developing pelvic fin are separate and distinct from the muscle of the somite (C, M, and W). Immediately before pelvic fin formation epithelial buds (mb) head the myotomal extension (me) (D, E, F, N, O, X, Y). The pelvic fin muscles (pfm) have formed within the pelvic fin and are separate from the myotomal extension (me) (G, H, I, P, Q, Z, AA, BB). myoD is restricted to individual, post-migratory, differentiating pelvic fin muscles (R). lbx1 positive cells (purple) at the position of the forming pelvic fin muscles (pfm) in lungfish (DD). Lbx1 expression in 14 dph pelvic fin of P. spathula, inset is a cross-section of the pelvic fin at the same stage, revealing lbx expression in the muscle masses (J). Lbx1 positive (blue) precursors in the tip of the extension position of the future pelvic fin muscles in D. rerio at 8 mm TL (S) and 9 mm TL (T). Lbx1-positive precursors in stage 50 pelvic fin bud of N. forsteri (DD). (ep, epithelial bud; me, myotome extension; pf, pelvic fin; pfm, pelvic fin muscle).