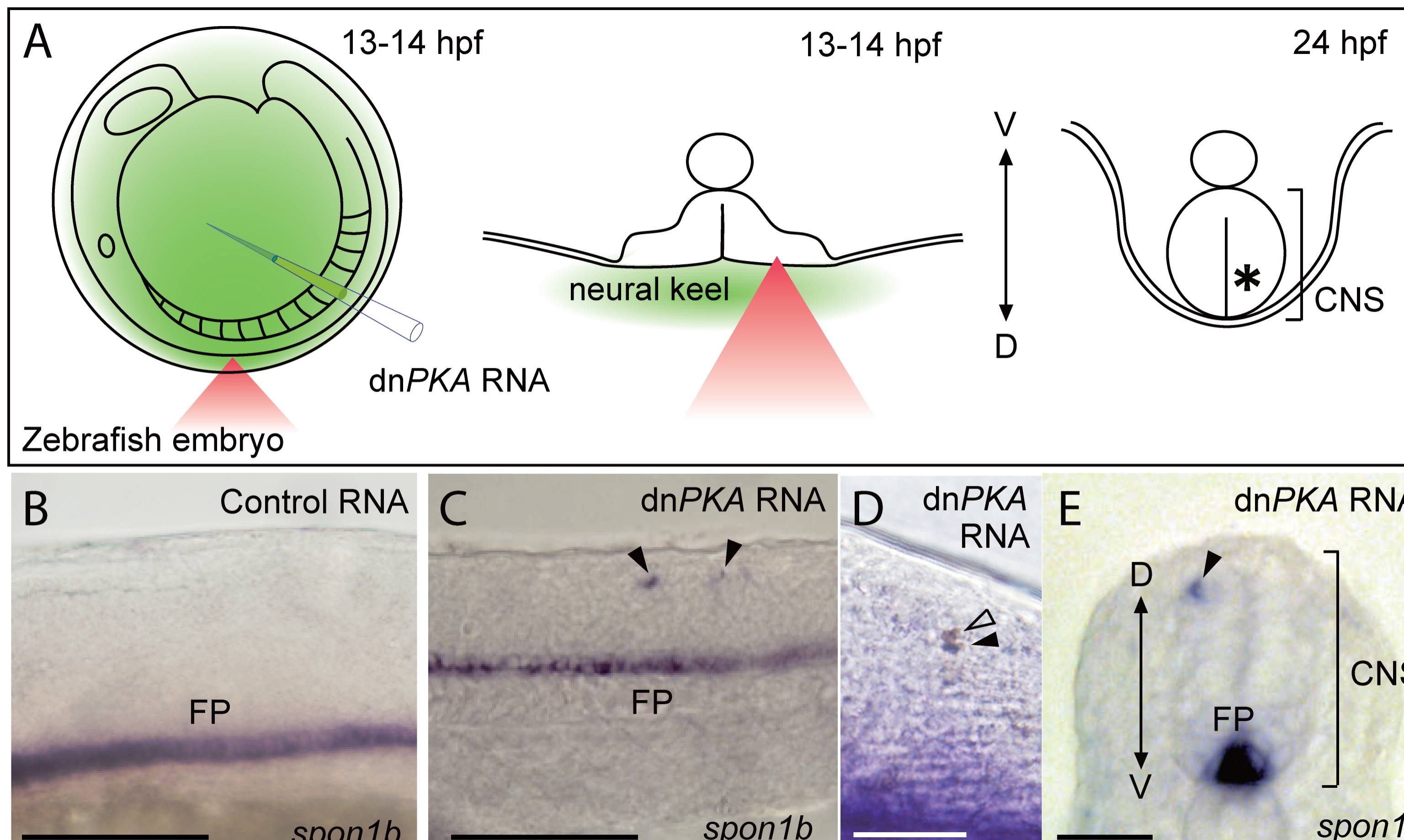
Fig. 4 Manipulation of the fate of targeted cells in zebrafish embryos.
Targeted introduction of dnPKA mRNA induced floor plate marker gene expression in single dorsal neurons of zebrafish embryos. (A) Schematic illustration of dnPKA mRNA delivery to single dorsal neurons of zebrafish embryos. dnPKA mRNA was injected into the cavity between the chorion and the surface of embryo, and dorsal neurons in the neural keel (center) were irradiated at 13–14 hpf with a femtosecond laser pulse (red triangle). Irradiated embryos were fixed at 24 hpf (right panel) and processed for in situ hybridization. (B–E) Expression of the floor plate marker spon1b in embryos injected with control EGFP RNA (B) and dnPKA RNA (C–E) at 24 hpf. (B–D) Lateral view; (E) transverse section. In the control embryo (B), spon1b transcripts were detected only in the floor plate. In the dnPKA RNA-injected embryo, ectopic spon1b signals were observed in individual cells (arrowheads in C, E). (D) Expression of the floor plate marker spon1b (purple) and localization of biotin-dextran (brown) in embryos injected with dnPKA RNA at 24 hpf. Ectopic expression of spon1b was only detected in cells photoporated with biotin-dextran (black arrowhead). Although dextran was also observed in the adjacent dividing cell (open arrowhead), ectopic spon1b expression was barely detected in this cell. CNS, central nervous system; D, dorsal; FP, floor plate; V, ventral. Scale bars: 100 μm (B, C); 50 μm (D, E).