Fig. 1
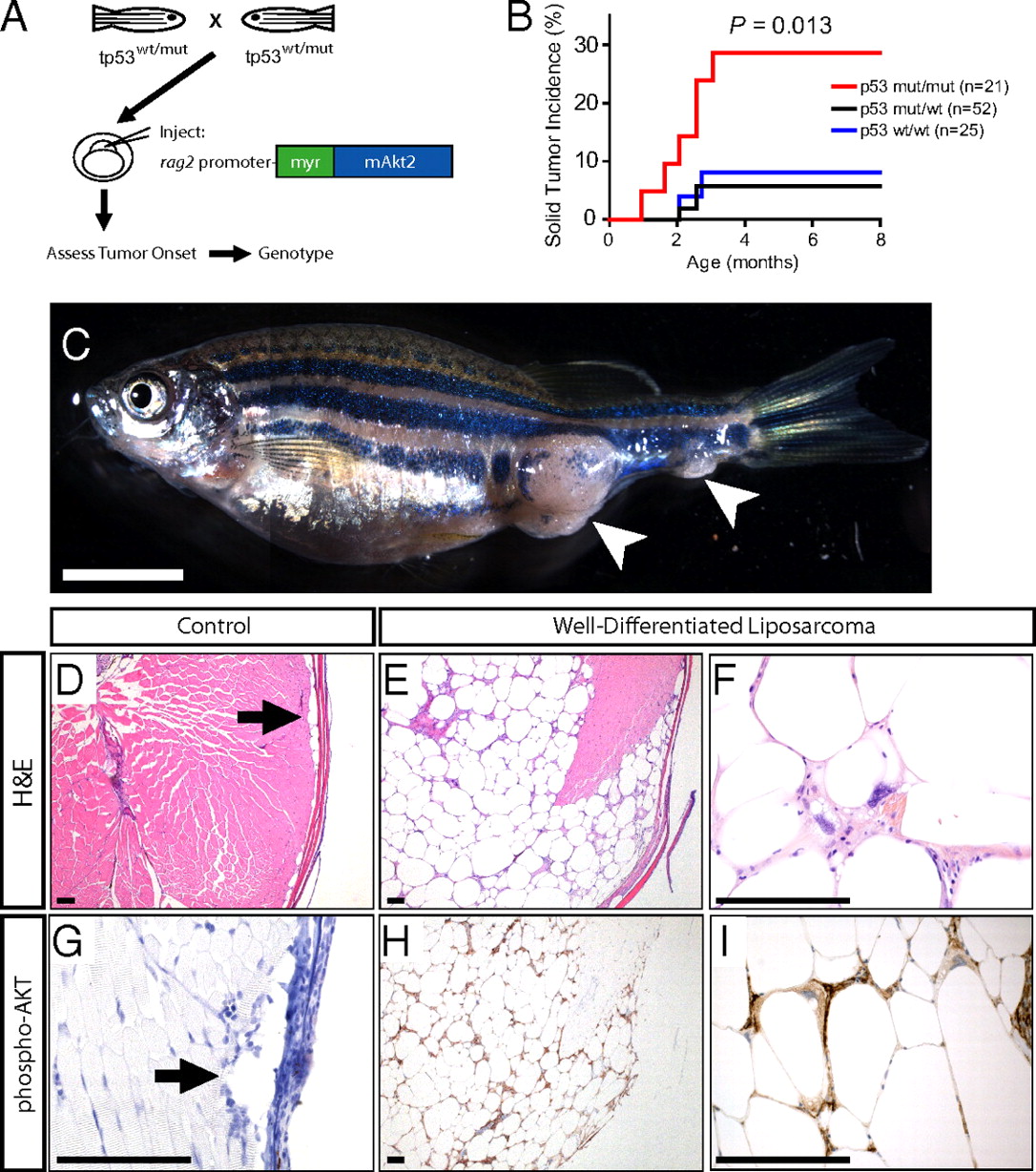
Constitutive Akt activation drives WDLPS in the zebrafish. (A) Experimental design. (B) Solid tumor incidence in p53 wild-type, heterozygous, or p53M214K homozygous mutant siblings injected with a rag2:myr-mAkt2 transgene at the one-cell stage. P value calculated via log-rank test. (C) Representative rag2:myr-mAkt2-injected zebrafish, which developed what appear to be two independent solid tumors. The animal shown was p53-homozygous mutant. (Scale bar, 5 mm.) Note that the image shown in (C) consists of merged adjacent photomicrographs. (D) Control H&E-stained zebrafish section. Arrow points to normal subcutaneous adipocytes. (E) Low-magnification view of an H&E section through the zebrafish shown in C, demonstrating a locally invasive mass consisting of well-differentiated adipocytes with significant variation in cell size. (F) High-magnification view of H&E section demonstrating a representative lipoblast scattered throughout these tumors, characterized by a multivacuolated cytoplasm and large hyperchromatic pleomorphic nuclei. (G) Phospho-AKT immunohistochemistry on a control zebrafish section. Arrow points to normal subcutaneous adipocytes, which lacked detectable pAKT staining. (H and I) Phospho-AKT immunohistochemistry on tumor sections from the zebrafish shown in C, revealing strong immunoreactivity for phospho-AKT in tumor cells of rag2:myr-mAkt2-transgenic zebrafish. (Scale bars, 100 μm.)