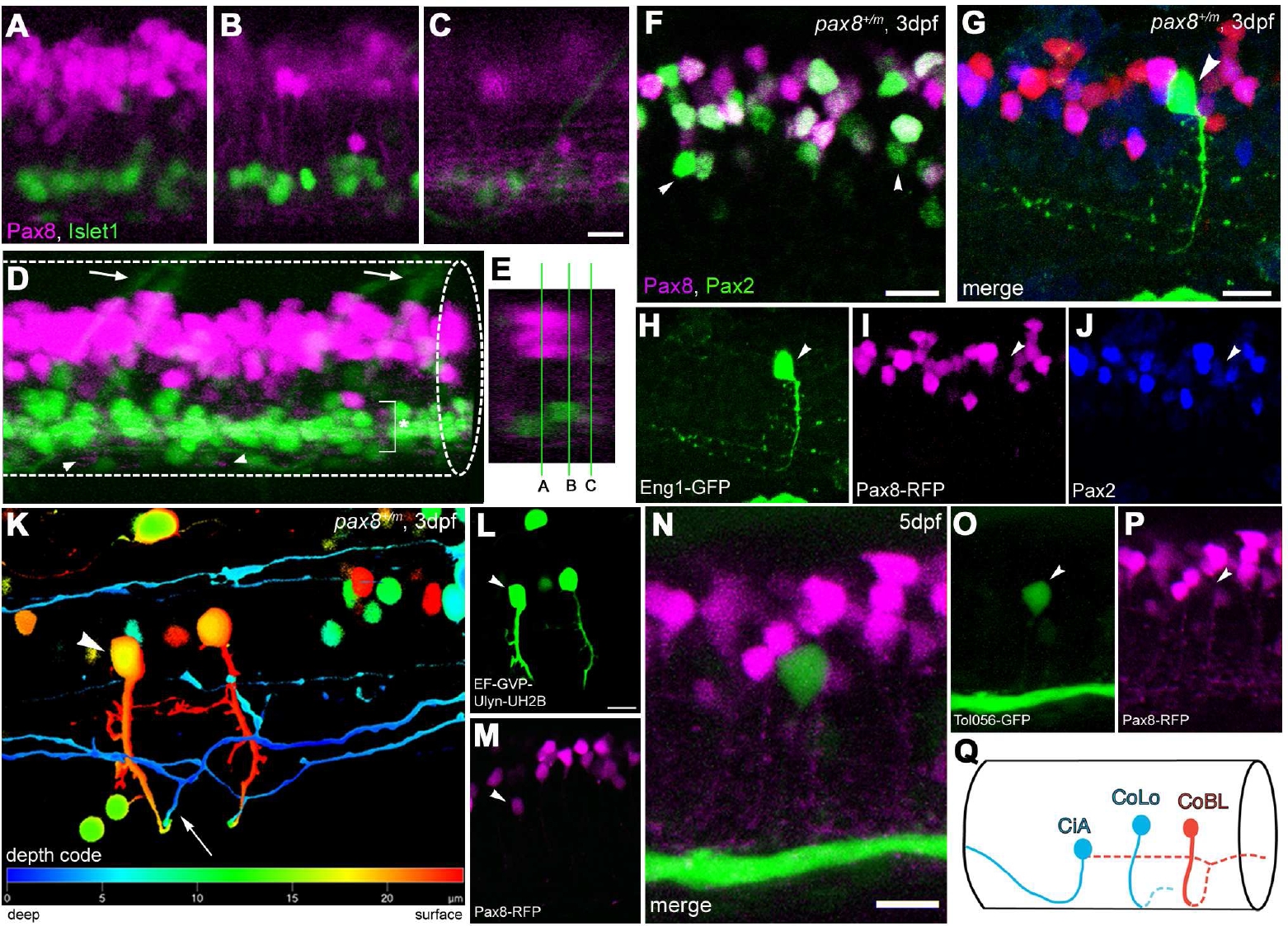
Fig. s4
(Magenta/Green version of Figure. 6 for the assistance of color blind readers.) Interneurons in the spinal cord expressing pax2a or pax8. A-E: RFP (+) neurons are detected in the dorsal portion of the spinal cord; RFP (red), islet-1:GFP (green). Single place confocal images (A, B, C) show the position of RFP(+) cells and islet-1 expressing secondary motor neurons. Scale: 10 µm. D is the 3D reconstruction. Arrowheads indicate commissural axons labeled by RFP and arrows indicate motor neuron axons labeled by GFP. The area with an asterisk has a plexus-like structure of RFP (+) fibers. An optical cross section (E) displays the level of confocal planes corresponding to A, B and C. F: Pax8+/m fish stained with anti-Pax2; RFP (red), anti- Pax2 (green). Arrowheads are Pax2 (+) cells without RFP. Scale: 10 μm. G-J: CiA neurons express Pax2 but lack RFP expression. G is a stack of confocal images with eng1-GFP (green), RFP (red) and Pax2 (blue). H-J are single plane images to show that the GFP (+) cell is Pax2 (+) but RFP (-). Scale: 10 μm. K, L, M:.CoBL neurons express RFP. K is a stack of confocal images in depth coding. The cell with an arrow has the characteristic axon pattern of CoBL. In single planes, the GFP (+) cell is also RFP (+) (L and M). Scale: 10 μm. N, O, P: CoLo neurons labeled with GFP (green) in Tol-056 fish do not express RFP (red). N is a merged image. O and P show that the marked cell expresses GFP but not RFP. Scale: 10 μm. Q: Schema of CiA, CoLo and CoBL interneurons in the spinal cord. The position of the cell body and the axon projection are shown. Rostral to the left. Note that CiA and CoLo (blue) do not express RFP, while CoBL (red) express RFP.