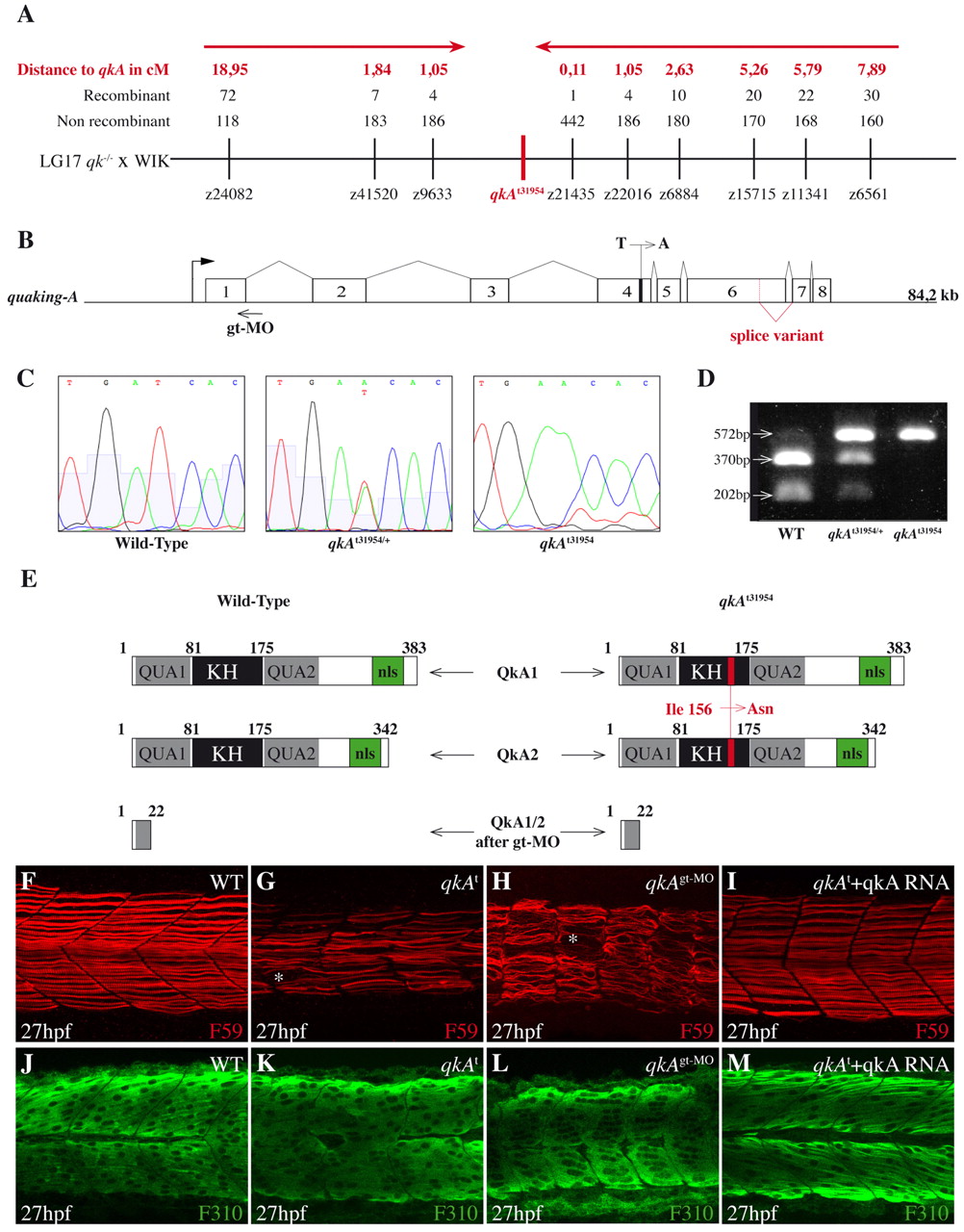
Fig. 2
Molecular and functional characterization of the qkA locus. (A) Genetic mapping of zebrafish quaking A (qkA). On chromosome 17, the qkAt31954 mutation is linked to markers z9633 and z21435, delineating a candidate genomic region of ~100 kb that contains qkA. Red arrows indicate the directions of mapping progression. (B) qkA gene structure. qkA includes eight exons. The alternative splicing site and the positions of the qkAt31954 mutation in exon 4 and of the qkAgt-MO are indicated. (C) Chromatogram showing the single base change in qkAt31954 mutants. (D) qkAt31954 mutation leads to the loss of an RFLP site (BclI). The qkA region was PCR amplified from genomic DNA and digested with BclI, which normally cuts a 572 bp fragment into 370 bp and 202 bp fragments. (E) Structure of predicted QkA protein isoforms in WT, mutant and qkAgt-MO embryos. The t31954 mutation leads to the Ile156Asn amino acid change (red) in the KH domain. KH, K homology domain; nls, nuclear localization signal. (F-M) qkAt31954 mutation can be rescued by qkA mRNA injection and is phenocopied by qkAgt-MO. WT, qkAt31954 mutants or qkA morphants, untreated or injected with qkA mRNA, were fixed at 27 hpf and processed as in Fig. 1A-D. Asterisks, gaps in slow muscle cells.