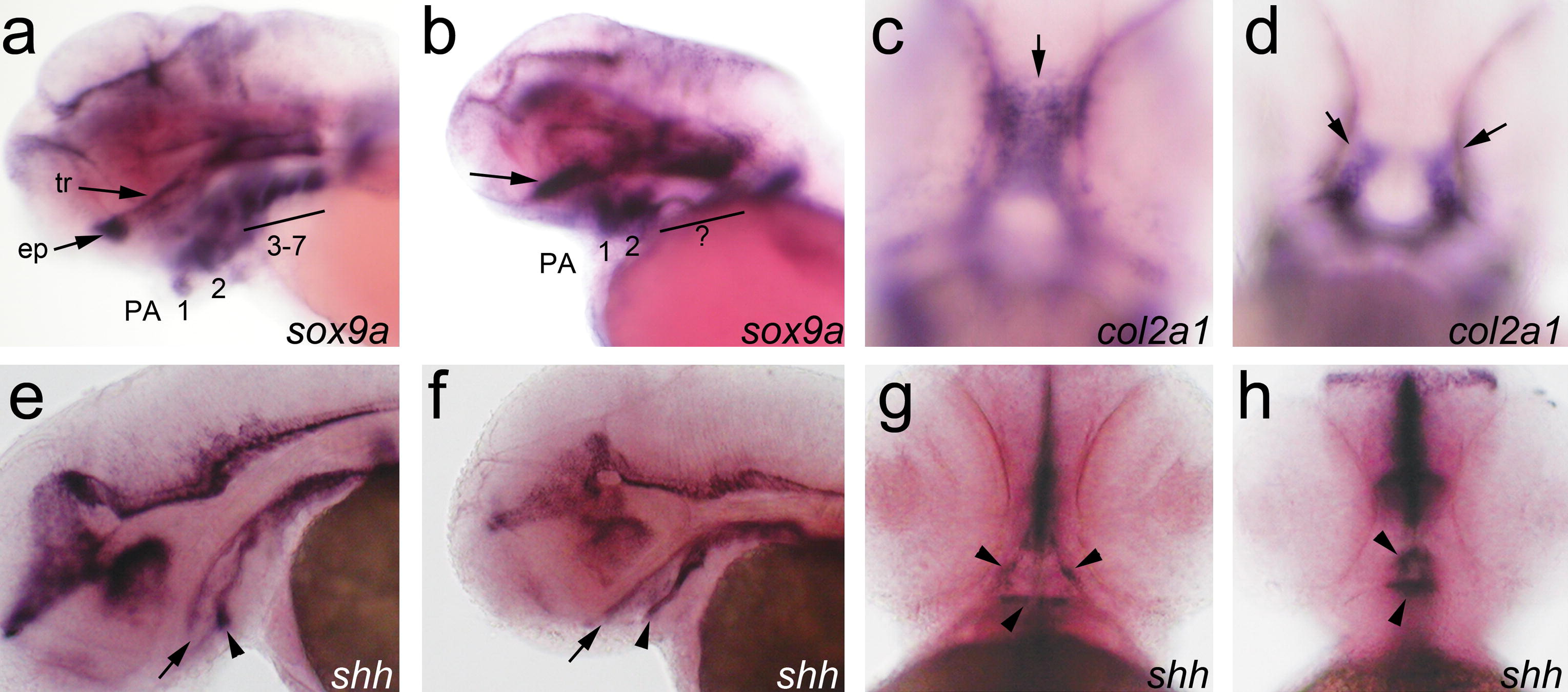
Fig. 7 Knockdown of wnt9a results in late craniofacial phenotypes. Embryos injected with wnt9a mismatch control (MM) (a, c, e and g), and translation-blocking morpholino (MO) (b, d, f and h). Embryos are mounted in lateral view with head toward left (a, b, e–h) and in ventral view with head toward top (c and d). Transcripts of sox9a (a and b) at 3 dpf, col2a (c and d) at 2 dpf, and shh (e–h) at 2 dpf are detected by whole mount RNA in situ hybridization. The truncated trabeculae and absent ethmoid plate are confirmed by comparison of sox9a expression between MO (b) and MM control (a). In the wnt9a morphant, sox9a expressing cells do not elongate to form the trabeculae, and there is no ethmoid plate (b, arrow). The expression of sox9a in the posterior pharyngeal arches is also absent (b, bar). The expression of col2a is present but aberrantly located in the wnt9a morphant, distinguishable from MM control as early as 48 hpf. In the MM control, col2a expression prefigures the trabeculae and the ethmoid plate (c), whereas in the morphant, the cranial neural crest cells are lateralized in linear groups (d). Oral epithelium express shh in a wildtype pattern in the MM control and the morphant, outlining the stomodeum (g, arrowheads). The stomodeum forms in the wnt9a morphant, although the shape is altered (f, arrowheads), and is continuous to the foregut, with shh expression outlining the roof (e, f, arrows) and floor (e, f, arrowheads) of the oropharynx.
Reprinted from Mechanisms of Development, 128(1-2), Curtin, E., Hickey, G., Kamel, G., Davidson, A.J., and Liao, E.C., Zebrafish wnt9a is expressed in pharyngeal ectoderm and is required for palate and lower jaw development, 104-115, Copyright (2011) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Mech. Dev.