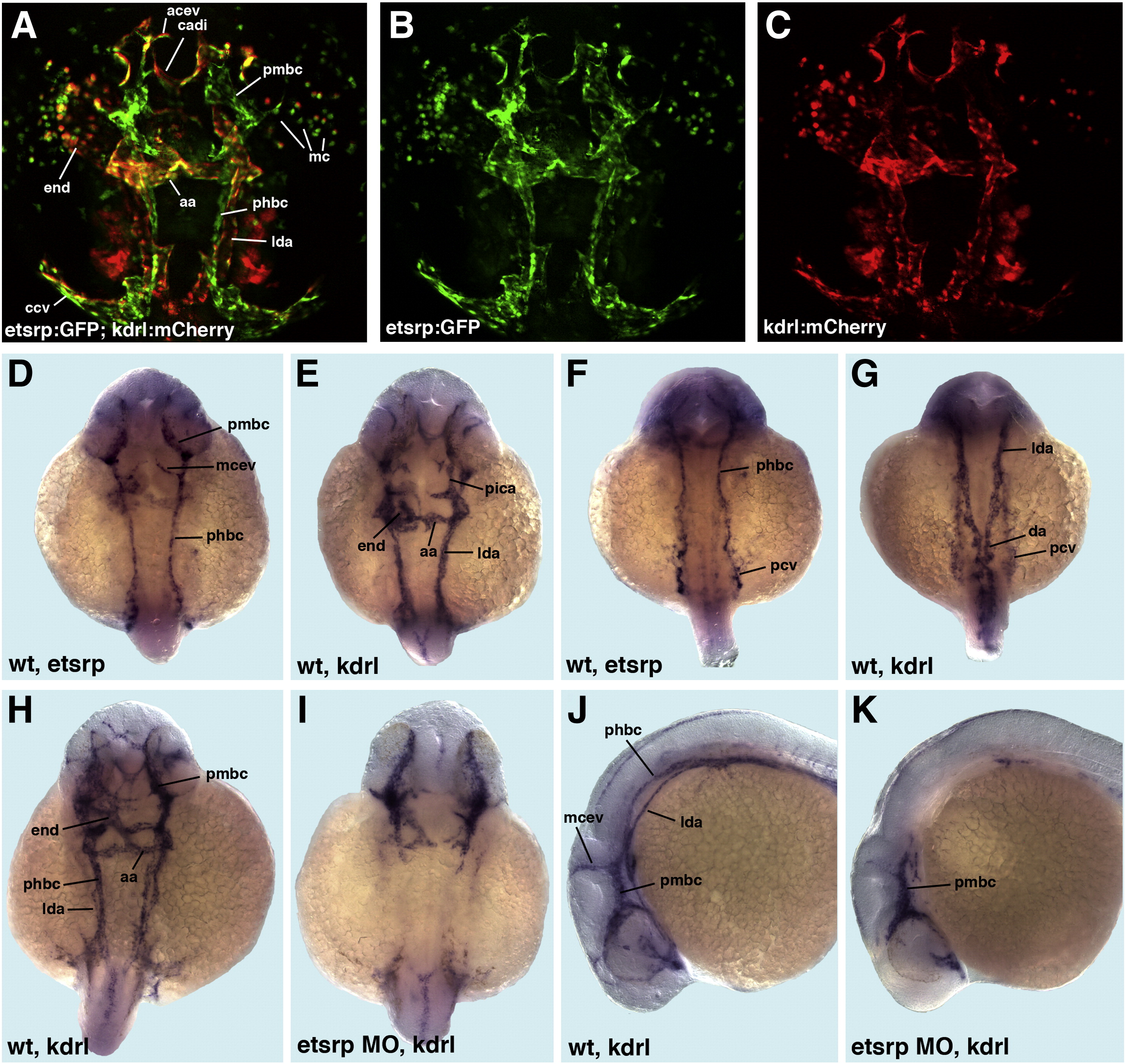
Fig. 8 Etsrp expression is enriched in venous cranial vessels while kdrl shows preferential arterial expression. (A–C) Anterior part of etsrp:GFP; kdrl:mCherry transgenic embryo at 24 hpf, dorsal view, anterior is to the top. (A) Merged image; (B) GFP channel; (C) mCherry channel. Note that venous vessels in the midbrain and hindbrain regions such as pmbc and phbc display strong GFP and weak mCherry expression while arterial vessels such as lda display weak GFP and strong mCherry expression. The most rostral vessels such as acev are positive for both GFP and mCherry. (D–G). In situ hybridization for etsrp (D,F) and kdrl (E,G) expression; dorsal view of the forebrain–midbrain region (D,E) and the hindbrain region (F,G) at 24 hpf. Anterior is to the top. Note that venous vessels in the midbrain and hindbrain regions such as pmbc, mcev, and phbc and the anterior part of pcv display intense etsrp expression while arterial vessels such as lda, aa, and pica and the anterior part of da display strong kdrl expression. (H–K). Both arterial and venous vessels are absent or reduced in etsrp morphants as analyzed by kdrl expression. (H,I) Dorsal view of the anterior region, anterior is to the top; (J,K) lateral view of the anterior region, anterior is to the left. (H,J) Control uninjected embryos, (I,K) etsrp morphants. Note that both arterial and venous vessels such as phbc and lda are absent in etsrp morphants. Only vessels that are closest to the MOC and the ROC such as pmbc partially form.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 348(1), Proulx, K., Lu, A., and Sumanas, S., Cranial vasculature in zebrafish forms by angioblast cluster-derived angiogenesis, 34-46, Copyright (2010) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.