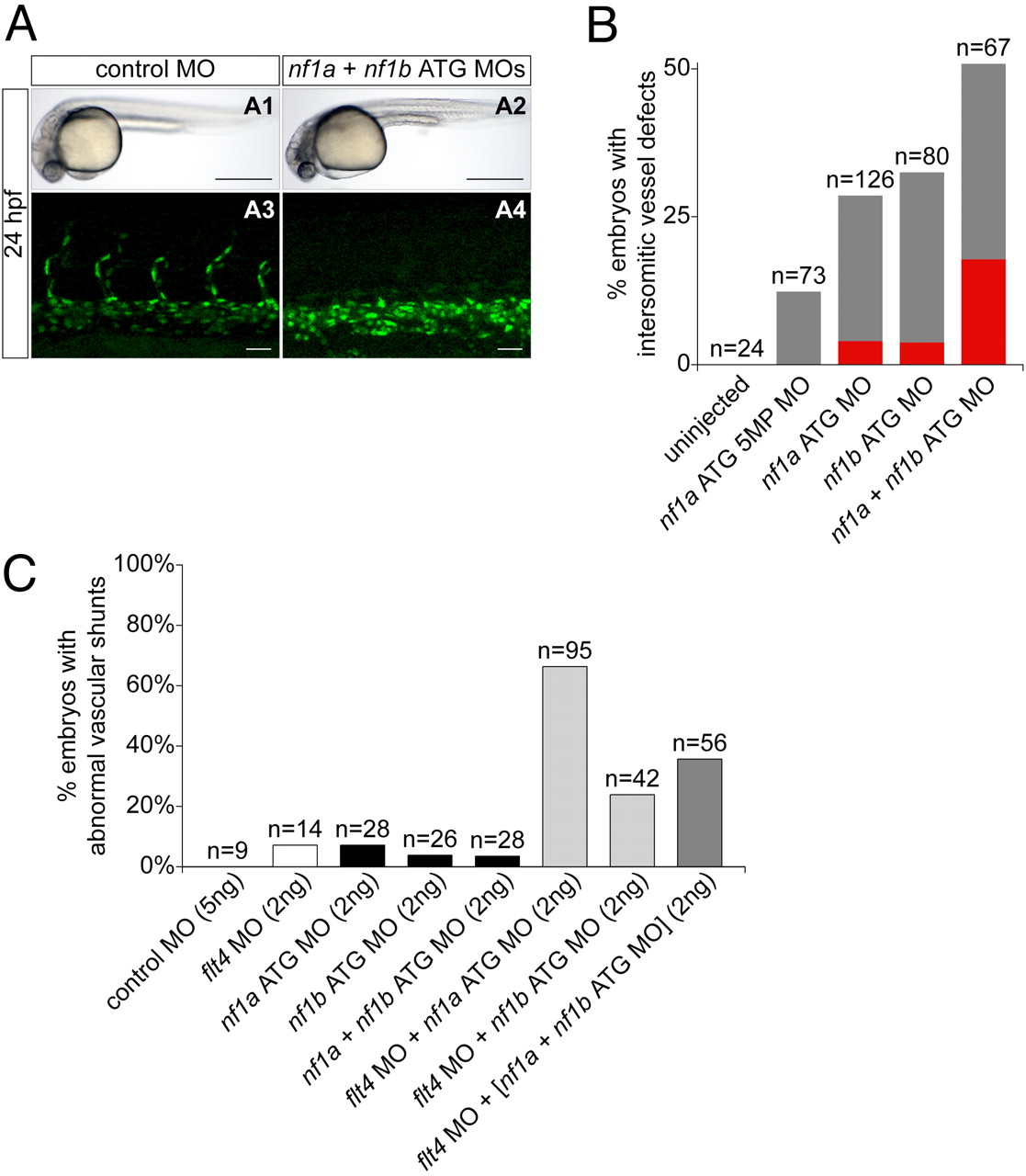
Fig. 5 MO knockdown of nf1a, nf1b, or both together result in vascular defects at 24 at 48 hpf. (A and B) Analysis and quantification of vascular defects at 24 hpf in uninjected and morphant Tg(fli:negfp)y7 (endothelial-specific nuclear GFP transgenic) zebrafish embryos. Control MO- (A1) and combined nf1a/nf1b MO-treated (A2) zebrafish embryos appear similar by gross morphological analysis at 24 hpf. (Scale bars: 500 μm.) Development of intersomitic vessels is deficient at 24 hpf in nf1a/nf1b combined morphants (A4) when compared with controls (A3). (Scale bars: 25 μm.) (B) Intersomitic vessel formation between somites 17–30 at 24 hpf was scored as absent (red), intermediate (gray), or normal following administration of 2 ng of the indicated MO(s). (C) MO-mediated knockdown of flt4, providing a sensitized background for the detection of vascular defects, was combined with nf1a, nf1b, and nf1a + nf1b ATG MO knockdown. Twenty-four to 85% of combined flt4/(nf1a, nf1b, nf1a + nf1b) MO-treated embryos display abnormal vascular shunts compared with 3–8% of individual flt4, nf1a, nf1b, or nf1a + nf1b MO-treated embryos.
Image
Figure Caption
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA