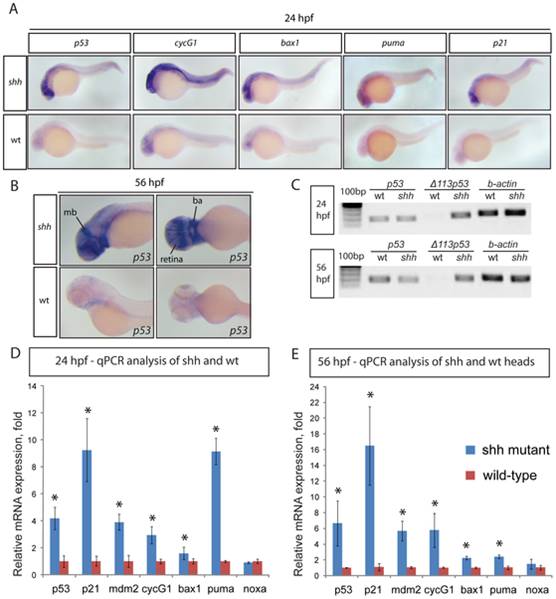
Fig. 1 (A) 24 hpf wild-type and shh-/- mutant embryos were in situ hybridised with probes against p53, cyclinG1, bax1, puma and p21 mRNAs. These p53 target genes are expressed at a higher level in the shh-/- mutant in neural tube, retina and somites than in wild-type embryos. (B) 56 hpf wild-type and shh-/- mutant embryos were hybridized with the probe against p53 mRNA. The hybridizations show increased expression of p53 in shh-/- mutant compared to wild-type embryos in the brain, retina and branchial arches. The following structures are labelled: retina, midbrain (mb) and branchial arches (ba). (C) p53 transcript isoforms in shh-/- mutant and wild-type at 24 and 56 hpf were analysed by semi-quantitative PCR assays for full-length p53, Δ113 p53 transcripts and beta;-actin transcript as a loading control. At both stages, full-length p53 and β-actin transcripts were expressed at similar levels in wild-type and mutant samples, whereas Δ113 p53 was strongly upregulated in shh-/- mutant samples. (D, E) qPCR assays for p53, p21, mdm2, cyclinG1, bax1, puma, noxa and gapdh were performed at 24 hpf (D) and 56 hpf (E) on wild-type and shh-/- mutant embryos. cDNA from whole embryos was used for 24 hpf samples and cDNA from embryo heads was used for 56 hpf samples. Gene expression was normalized using gapdh expression as reference. The panels show p53 target gene expression in wild-type and shh-/- mutant embryos (D, E). Error bars represent standard deviation and an asterisk indicates statistical significance. There are significant expression differences between wild-type and shh-/- mutant samples (t-test, * - p<0.05) for all genes except noxa. qPCR assays were performed in triplicates on three different clutches of embryos and standard deviations are shown.
Image
Figure Caption
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ PLoS One