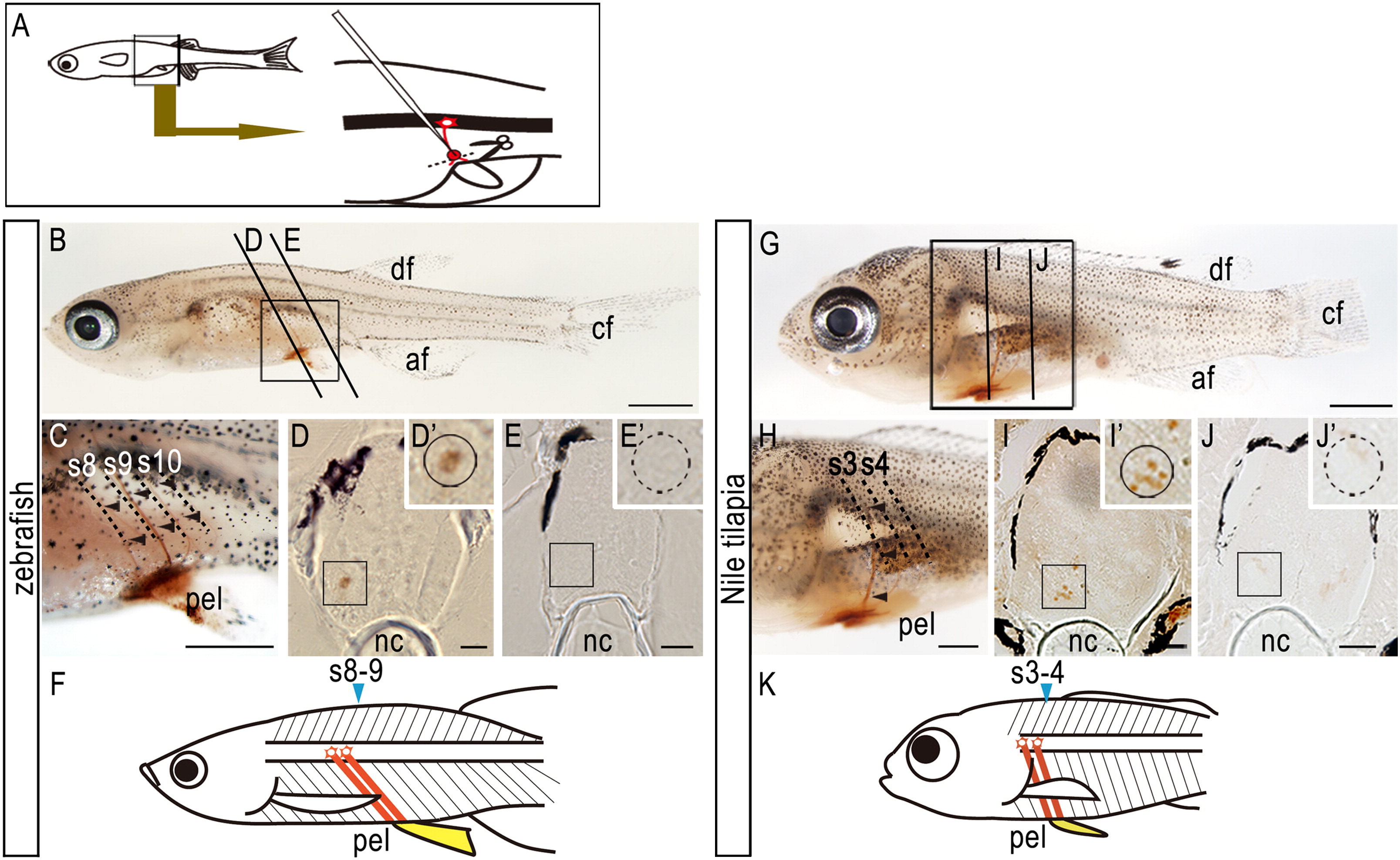
Fig. 6 Axial positions of the spinal cord and pelvic fins in zebrafish and Nile tilapia. (A) Biotin-conjugated dextrans were injected into the proximal region of the pelvic fins to label motoneurons (see Materials and methods). (B-F) Zebrafish. (G-K) Nile tilapia. (B-E, G-J) Patterns of motoneurons that innervate the pelvic fin muscles in (B-E) zebrafish larvae and in (G-J) Nile tilapia larvae. (C, H) Details of labeled motoneurons in (B) and (G), respectively. Note that the biotin-labeled motoneurons innervate the pelvic fin (arrowheads). (D, E) Sections of the spinal cord opposite 8th-9th (D) and 10th (E) segments of zebrafish indicated in (B). (I, J) Sections of the spinal cord opposite 3rd and 4th (I) and 5th (J) segments of Nile tilapia indicated in (G). Each inset in (D), (E), (I) and (J) shows a higher magnification of the boxed area in each panel. Cell bodies connected into the pelvic fins are seen in the spinal cord lying above the pelvic fins (insets in D and I) but not in the posterior spinal cord (insets in E and J). (F, K) Schematic diagrams of the axial position of the spinal cord and pelvic fins in zebrafish (F) and Nile tilapia larvae (K). Motoneurons lying above the pelvic fins innervate the pelvic muscles. Somites/segments adjacent to the pelvic fins at the fin bud stage are indicated in blue. af, anal fin; df, dorsal fin; cf, caudal fin; nc, notochord; pec, pectoral fin; pel, pelvic fin. Scale bars: 1.0 mm for panels (B), (C), (G), and (H); 50 μm for panels (D), (E), (I), and (J).
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 347(1), Murata, Y., Tamura, M., Aita, Y., Fujimura, K., Murakami, Y., Okabe, M., Okada, N., and Tanaka, M., Allometric growth of the trunk leads to the rostral shift of the pelvic fin in teleost fishes, 236-245, Copyright (2010) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.