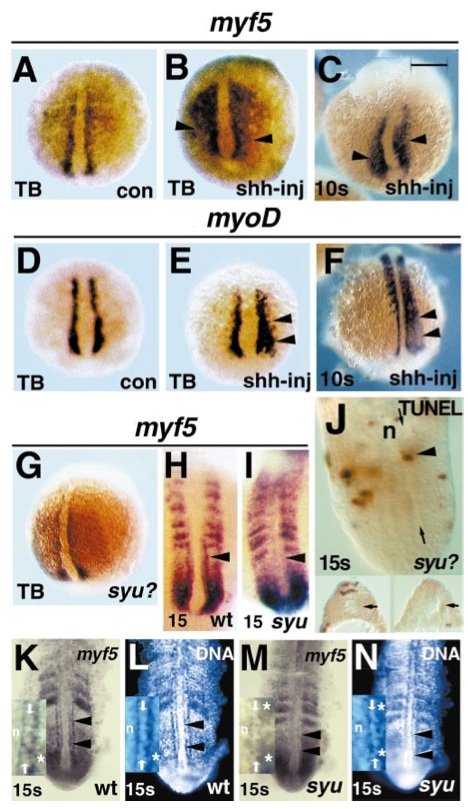
Fig. 3 myf5 is maintained in adaxial cells by Sonic hedgehog from the ventral midline. Injection of RNA encoding shh into two to four cell zebrafish embryos causes widespread ectopic expression of both myf5 (A–C arrowheads) and myoD (D–F arrowheads) in the lateral presomitic mesoderm at tailbud (A, B, D, E) and 10 somite (C, F) stages. myf5 expression appears unaffected by lack of Sonic hedgehog in clutches of tailbud stage embryos from a syu heterozygote cross (G, a randomly selected embryo from 45 in such a cross, shown in three-quarter dorsal view, posterior at bottom). In adaxial cells in the presomitic mesoderm of the future yolk extension region of 15 somite syu embryos, myf5 mRNA levels are reduced compared to wild type (H, I arrowheads), although lateral presomitic mesoderm and somitic expression appears unaffected. (J) TUNEL staining revealed few apoptotic cells in 15 somite embryos from a syu heterozygote cross; dorsal view at mount. Single TUNEL-reactive cells (arrowhead) were detected in adaxial positions (between arrows) adjacent to the notochord (n) in about 10% of embryos. Serial transverse sectioning of TUNEL-stained embryos confirmed the presence of adaxial cells (insets, arrows, dorsal to top) and the low frequency of adaxial apoptosis. The decline in adaxial myf5 mRNA in a syu embryo (M) compared to wild-type sibling (K) is not due to loss of the expressing cells, because visualisation of DNA-containing nuclei in the same individual embryos reveals cells with normal adaxial morphology and position (L, N arrowheads). Insets in K–N show anterior presomitic mesoderm of 15 somite stage embryos, notochord at left (n). Rows of adaxial cell nuclei (between arrows) are clearly discernible in wild type, with myf5 signal outlining the nuclei (K, L). In syu mutant (M, N) a row of adaxial-like nuclei (between arrows) does not have cytoplasmic myf5 signal, but is morphologically distinguishable from nuclei in both nonexpressing notochord (n) and myf5-expressing lateral paraxial presomitic mesoderm (asterisks). All images show posterior at bottom in either wholemount (A–I, dorsal view) or at mount (K–N, ventral view after removal of yolk cells) embryos. Bar, 200 μm in A–G, 120 μm in H, I, 67 μm in K–N, 48 μm in J, 30 μm insets K–N.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 236(1), Coutelle, O., Blagden, C.S., Hampson, R., Halai, C., Rigby, P.W.J., and Hughes, S.M., Hedgehog signalling is required for maintenance of myf5 and myoD expression and timely terminal differentiation in zebrafish adaxial myogenesis, 136-150, Copyright (2001) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.