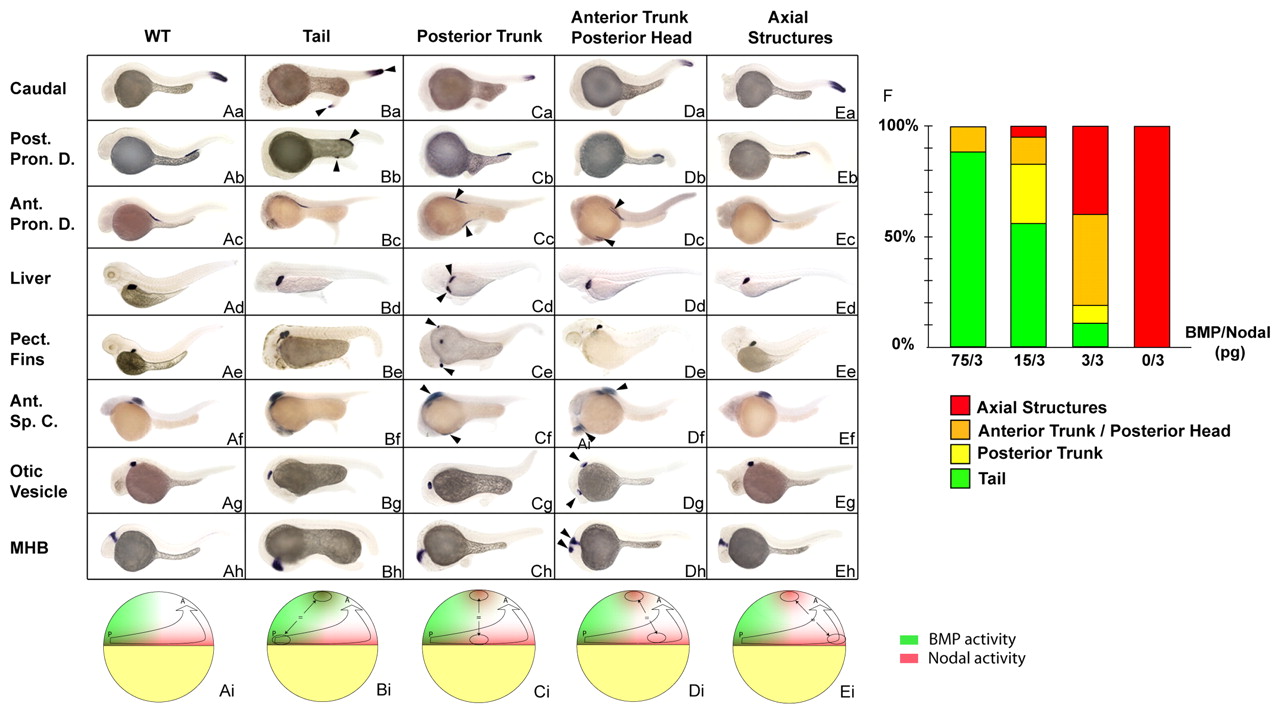
Fig. 4
Fig. 4 Simultaneous stimulation of Nodal and BMP activities recapitulates the organizing activities of the different marginal domains. (Aa-Eh) In situ hybridization with markers of caudal structures (hoxC13b, first row), posterior pronephric ducts (Post. Pron. D., slc12a3, second row), anterior pronephric ducts (Ant. Pron. D., slc4a2, third row), liver (fabp10, fourth row), pectoral fins (Pect. Fins, si:dkey-70p6.3p, fifth row), anterior spinal cord (Ant. Sp. C., rxrγ, sixth row), otic vesicles (starmaker, seventh row) and the midbrain-hindbrain boundary (MHB, engrailed 2, eighth row) on embryos co-injected with nodal and a range of bmp RNAs in an animal pole blastomere at the 128-cell stage and sorted based on the morphology of the induced secondary structures, as indicated at the top. WT embryo (Aa-h), embryo displaying a secondary tail (Ba-h), posterior trunk (Ca-h), anterior trunk/posterior head (Da-h) and axial structures (Ea-h). (Ai-Ei) Schematic representation of embryos at late blastula stage, dorsal to the right, depicting the type of marginal grafts at the animal pole of a host blastula that result in the formation of the structures indicated above the figure. Green, the ventral domain corresponding to high levels of BMP; red, the activity of Nodal at the blastula margin. (F) The frequency of the different classes generated after injection of various dilutions of bmp and nodal RNAs. Green, tail; orange, posterior trunk; yellow, anterior trunk/posterior head; red, notochord; WT, wild type; arrowheads, endogenous and ectopic structures formed. Lateral view. For each condition, at least 120 embryos were injected in two independent experiments.