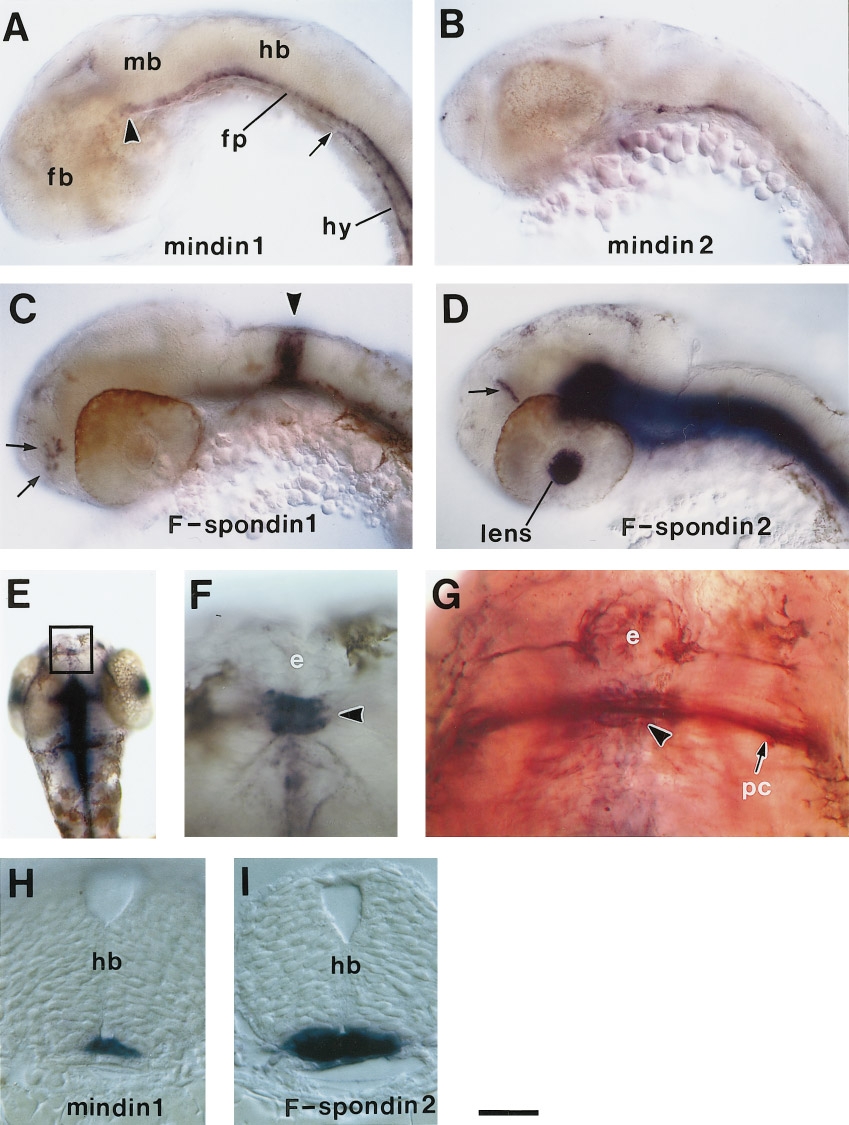
Fig. 6 mRNA expression of mindin/F-spondin family in the head region. (A–D) Lateral view of the head region stained with mindin1 (A), mindin2 (B), F-spondin1 (C), and F-spondin2 (D). Embryos in A and B are 26 h. Embryos in C and D are 28 h. An arrowhead in (A) indicates the rostral end of mindin1 expression in the floor plate. It extends up to, but not including, the forebrain. The arrow in (A) indicates the rostral end of mindin1 expression in the hypochord. It extends up to the caudal end of the hindbrain. An arrowhead in (C) indicates F-spondin1 expression in the rhombomere 4. Arrows in (C) indicate F-spondin1-expressing cells in the forebrain. An arrow in (D) indicates F-spondin2-expressing cells in the forebrain. (E) Dorsal view of a 36-h embryo stained for F-spondin2 mRNA. (F) A close-up view of the boxed region in E. F-spondin2 is expressed in a cluster of cells (arrowhead) just behind the epiphysis. (G) Dorsal view of a 32- h embryo double-stained for F-spondin2 mRNA and for acetylated α-tubulin. F-spondin2-positive signal (arrowhead) is present just beneath the posterior commissure. (H and I) Cross section of the hindbrain region of 28-h embryos stained for mindin1 mRNA (H) and F-spondin2 mRNA (I). fp, floor plate; hy, hypochord; fb, forebrain; mb, midbrain; hb, hindbrain; e, epiphysis; pc, posterior commissure. Scale bar, 100 μm in A–D, 180 μm in E, 30 μm in F and G, and 17 μm in H and I.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 192, Higashijima, S., Nose, A., Eguchi, G., Hotta, Y., and Okamoto, H., Mindin/F-spondin family: novel ECM proteins expressed in the zebrafish embryonic axis, 211-227, Copyright (1997) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.