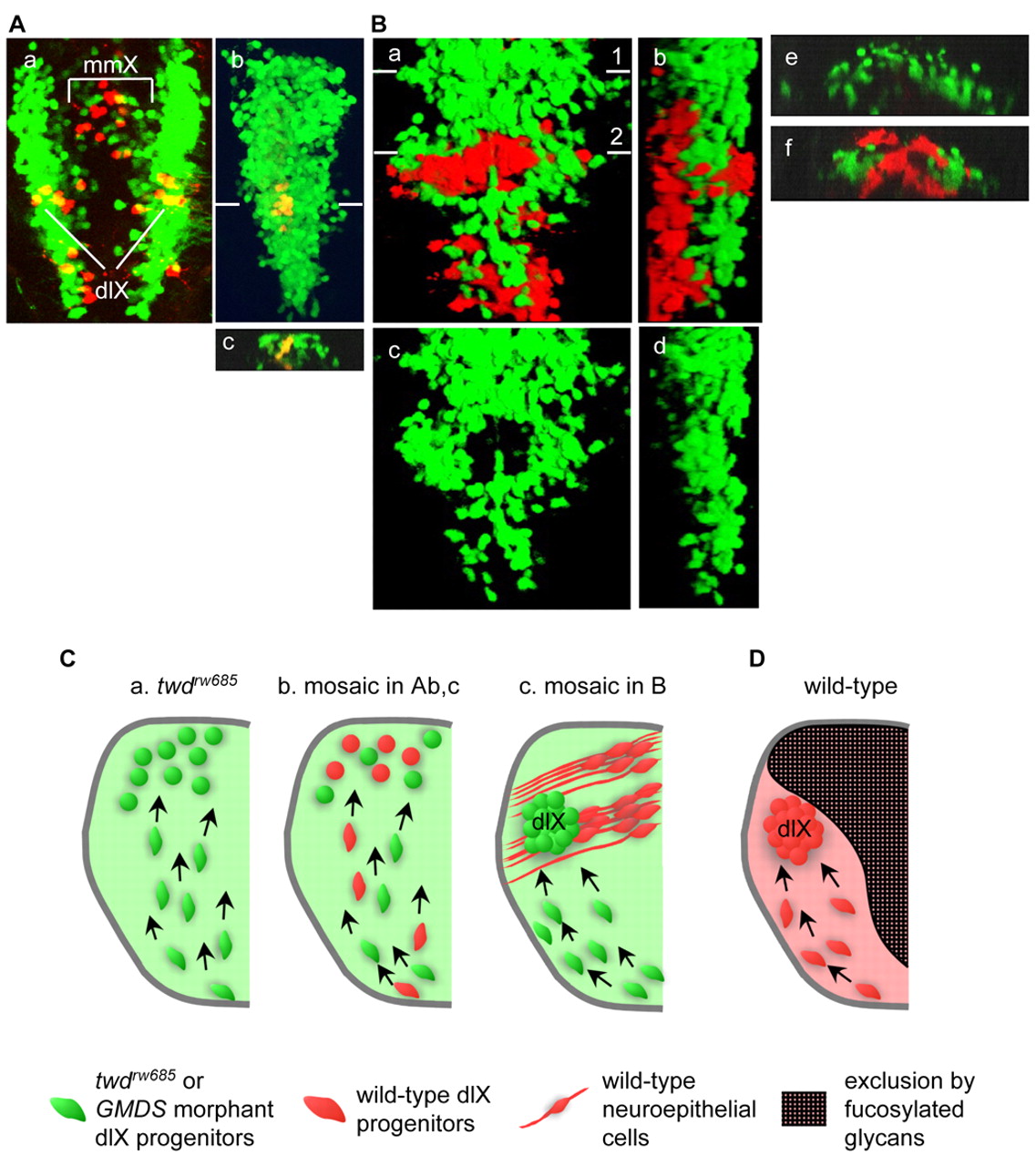
Fig. 10 Surrounding neuroepithelial cells regulate the migration of progenitors of the dorsolateral motor nuclei of the vagus (dlX). (A) The wild-type vagus motor neuron progenitors (yellow) were transplanted into wild-type (a) and the gmds morphant (b,c) hindbrain. Dorsal view (a,b; rostral towards the top) and cross-section (c; dorsal towards the top) at the level of the line shown in b. The embryos were observed at 48 hpf. dlX, dorsolateral motor nucleus of the vagus; mmX, medial motor nucleus of the vagus. (B) Wild-type cells (red) were transplanted into the dorsomedial region of the GMDS morphant hindbrain. In this case, the morphant vagus motor neuron progenitors migrated to their correct location (line 2 in a). Dorsal view (a; rostral towards the top) and lateral view (b; rostral towards the top, dorsal towards the right). To observe details of the transplanted embryos, pictures are shown without wild-type cells; c and d correspond to a and b, respectively. Cross-sections of transplanted embryos at the level of lines 1 (e) and 2 (f) in a. The embryos were observed at 48 hpf. (C) Relationship between neural progenitor migration and fucosylation in dlX formation in embryos of the twdrw685 mutant (a), the mosaic in A, parts b,c (b), and the mosaic in B (c). The twdrw685 and GMDS morphant and wild-type dlX progenitors are shown in green and red, respectively. The wild-type neuroepithelial cells are shown in red with the processes. (D) Model to explain how fucosylated glycans regulate the behavior of vagus motor neuron progenitors. There are three steps involved: differentiation near the ventral midline, migration in the dorsolateral direction, and cessation of migration and accumulation of the progenitors at their defined locations. During these developmental steps, dorsomedially distributed fucosylated glycan prevents the dlX progenitors from entering the dorsomedial region of the hindbrain. In the twdrw685 embryos, the progenitors show aberrant migration because this inhibition is lacking.
Image
Figure Caption
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Development