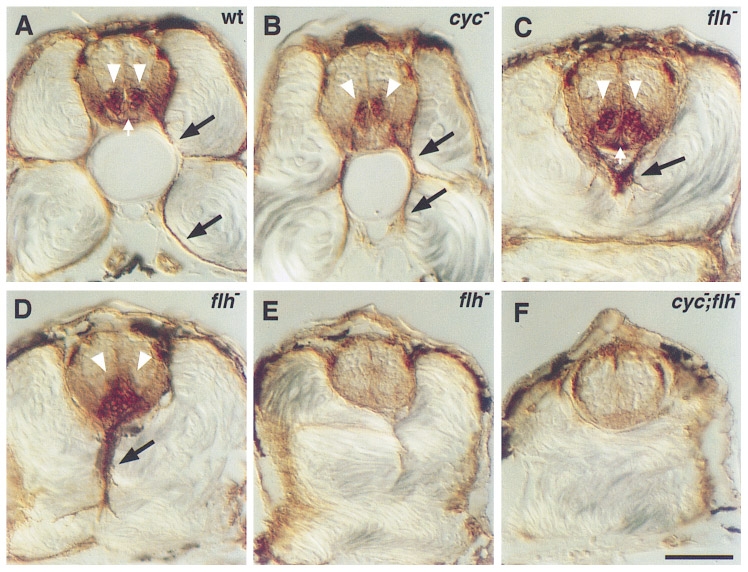
Fig. 1 Secondary motoneurons in mutant embryos. Antibody labeling (zn-5) of the Dm-grasp protein was used to characterize secondary motoneurons and floor plate in transverse sections through the trunk of wild-type and mutant embryos at 48 hr. Wild-type embryos (A) have two columns of secondary motoneuronal cell bodies in the ventral spinal cord (white arrowheads) and axons extending ventrally out of the spinal cord (black arrows). The floor plate, a triangular group of cells ventral to the secondary motoneuronal cell bodies, is also labeled (white arrow). In cyc mutants (B), the secondary motoneuronal cell bodies are often fused at the midline, but axons still extend out of the spinal cord. Floor plate is absent. In flh mutants (C, D, E), three patterns were observed. In some cases (C), the secondary motoneuronal cell bodies look normal and are separated by floor plate (white arrow). In other cases (D), bilateral clusters of cell bodies are fused across the midline and floor plate is visible. In both of these cases, axons extend out of the spinal cord, but their trajectories are aberrant (black arrows in C and D). In the third case (E), there are no secondary motoneuronal cell bodies, no axons, and no floor plate. In cyc;flh mutants (F), secondary motoneuronal cell bodies and axons as well as floor plate are absent. Scale bar, 50 μm.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 187(2), Beattie, C.E., Hatta, K., Halpern, M.E., Liu, H., Eisen, J.S., and Kimmel, C.B., Temporal separation in the specification of primary and secondary motoneurons in zebrafish, 171-182, Copyright (1997) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.