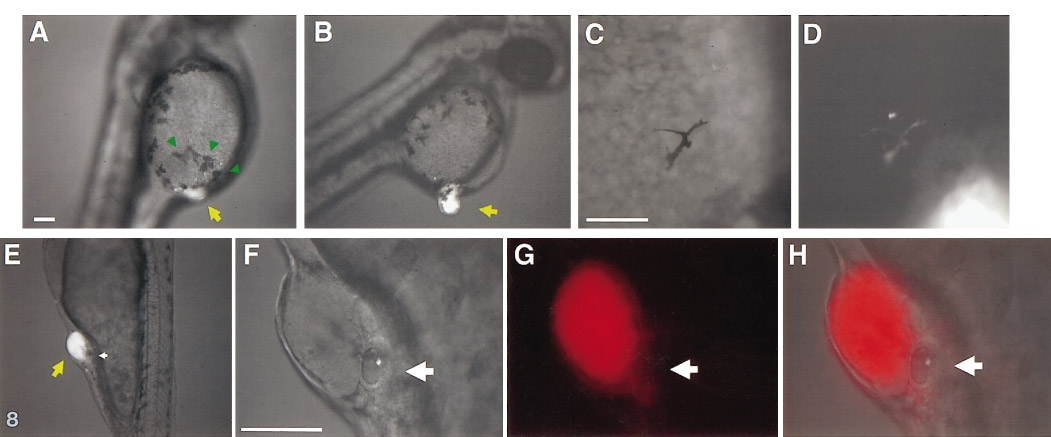
Fig. 8 Ectopically located hindbrain progenitors induce ectopic neural crest derivatives and otic vesicles. (A–D) Ectopic pigment cells are detected near 80H grafts of LRD-labeled tissues. (A) Ectopic pigment cells (green arrows) are present near the graft (yellow arrow); normally, the yolk is devoid of large pigment cells at this stage (compare left and right side of the yolk). (B–D) The majority of the ectopic pigment cells are host-derived, but occasionally, rhodamine-labeled (i.e., graft-derived) pigment cells are also seen. (E–H) Ectopic otic vesicles are formed adjacent to 80H grafts. Ectopic otic vesicles (E, magnified views F–H) can form in different regions of the ectoderm overlaying the yolk. (This embryo actually formed a pair of ectopic otic vesicles, one on either side of the graft. All ectopic otic vesicles are host-derived.)
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 197, Woo, K. and Fraser, S.E., Specification of the hindbrain fate in the zebrafish, 283-296, Copyright (1998) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.