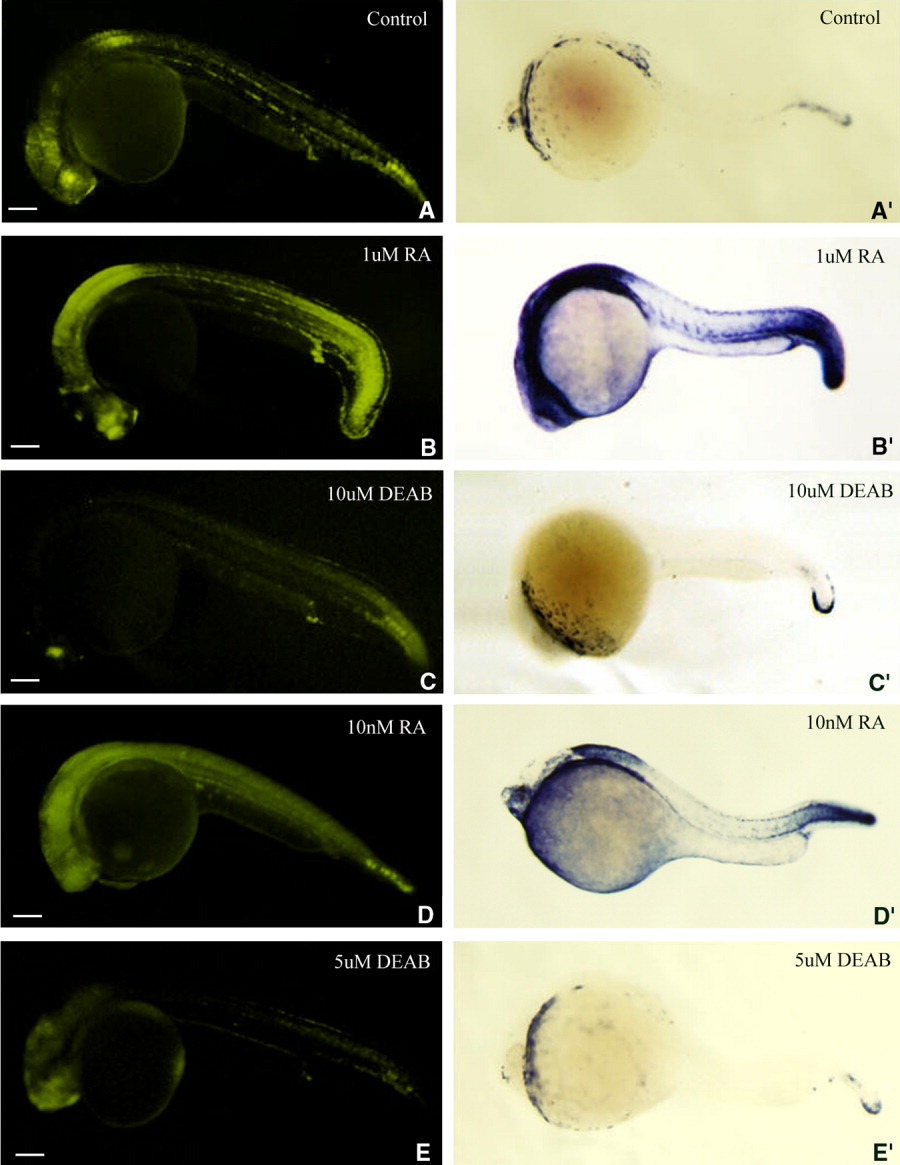
Fig. 6 Retinoic acid (RA) inducibility of enhanced yellow fluorescent protein (eYFP) expression in transgenic zebrafish embryos is similar to that of cyp26a1. B-E′: The transgenic embryos produced by a female wild-type zebrafish mated with a male transgenic zebrafish were treated with 1 μM RA (B,B′) or 10 μM DEAB (C,C′) for 6 hr starting from 18 hours postfertilization (hpf), or 10 nM RA (D,D′), or 5 μM DEAB (E,E′) for 24 hr starting from 0 hpf to examine whether the RA-induced expression of the transgene (B-E) is similar to that of cyp26a1 (B′-E′; revealed by whole-mount in situ hybridization) during zebrafish early development. A,A′: Untreated transgenic embryos were used as controls. Fluorescent images were photographed by a DP70 digital camera with 10-sec exposure time. Embryos are laterally viewed and positioned anterior left. In the embryos that were treated with 1 μM RA for 6 hr (B,B′), the greatly up-regulated expression was mainly seen in forebrain, anterior spinal cord, proctodeum, and whole tail (A,B,A′,B′). In the embryos treated with 10 nM RA for 24 hr treatment (D,D′), the up-regulated expression was almost in whole body but mainly seen in retina, anterior spinal cord and caudal notochord (A,D,A′,D′). When the embryos are treated with 10 μM DEAB for 6 hr (C, C′) or 5 μM DEAB for 24 hr (E,E′), the expressions of the transgene and cyp26a1 both are down-regulated mainly in retina, anterior spinal cord, and caudal notochord compared with wild-type embryos (A,A′). Scale bar = 100 μm.
Image
Figure Caption
Figure Data
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Dev. Dyn.