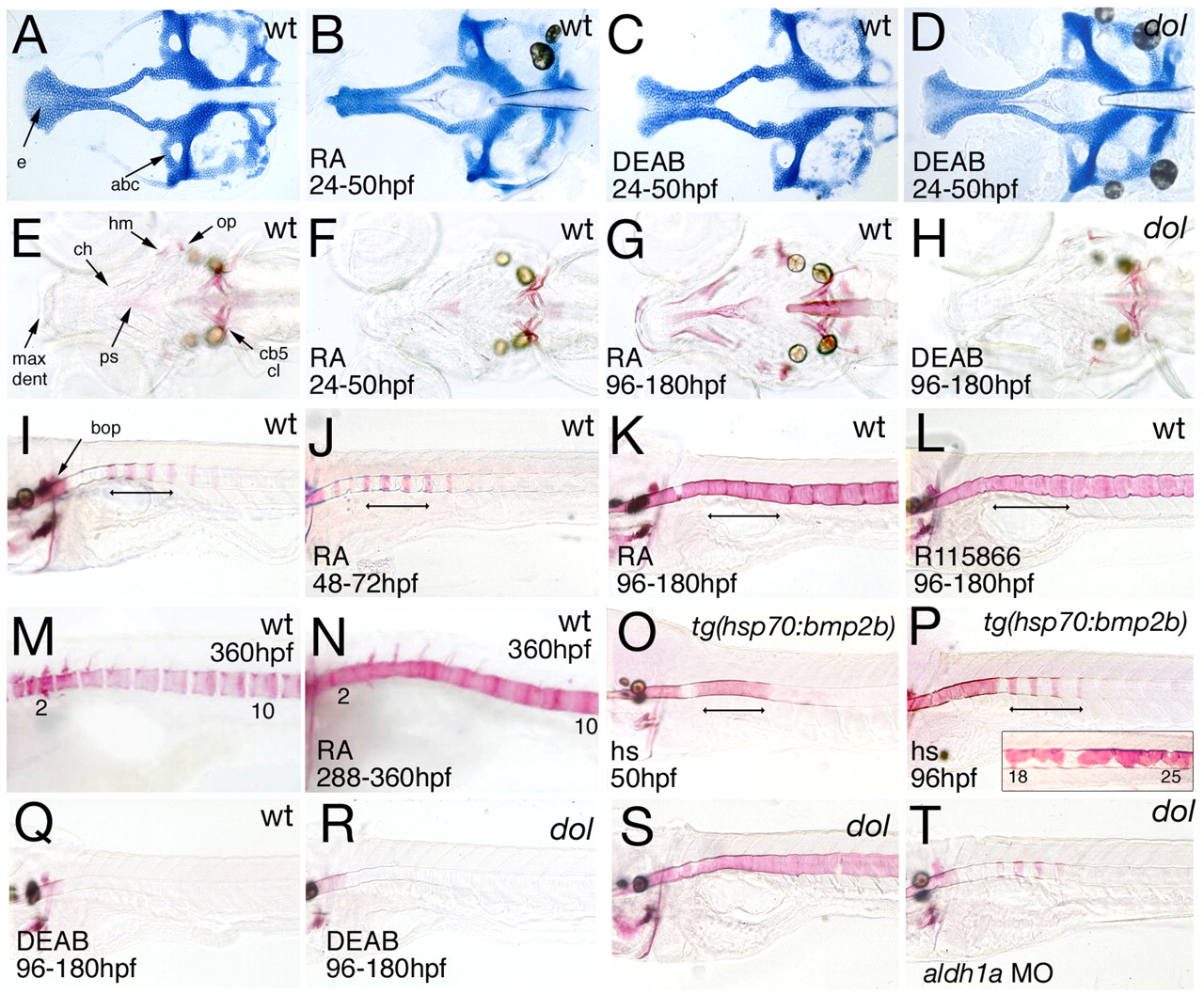
Fig. 7 Retinoic acid (RA) deficiency reverts, whereas RA excess phenocopies, the skeletal alterations of cyp26b1 mutants, with a pattern of axial hyperossification different from that caused by Bmp2b overexpression. Genotypes are indicated in upper right corners, treatments in lower left corners. (A-D) Flat-mounts of Alcian Blue-stained neurocrania after treatment from 24-50 hpf; 120 hpf, dorsal views. Note the absence of the medial ethmoid plate (e) in the RA-treated wild-type zebrafish (B), and the recovery of this structure in the DEAB-treated cyp26b1 mutant (D). (E-H) Alizarin Red-stained heads after treatment from 24-50 hpf (F) or from 96-180 hpf (G,H); 180 hpf, dorsal views. Late (G), but not early (F), RA treatment phenocopies hyperossification of craniofacial bones, whereas late DEAB treatment reverses the mutant phenotype and causes delayed ossification (H). (I-T) Alizarin Red-stained centra after treatment with RA (J,K,N), R115866 (L), DEAB (Q,R) or heat shock (hs; O,P) at indicated developmental stages, or after aldh1a MO injection (T); 180 hpf(I-L,O-T) or 360 hpf (M,N; vertebrae numbers indicated); lateral views. In I-P, the early-specifiying centra at the level of somites 3-6 are indicated by a bar. Inset in P shows precocious and unsegmented perichordal mineralization at somite levels 18-26 of the same bmp2b transgenic animal. See text for details. cb5, ceratobranchial 5 (with teeth); cl, cleithrum; den, dentary; max, maxilla; ps, parasphenoid; see also Figs 4, 5, 6.
Image
Figure Caption
Figure Data
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Development