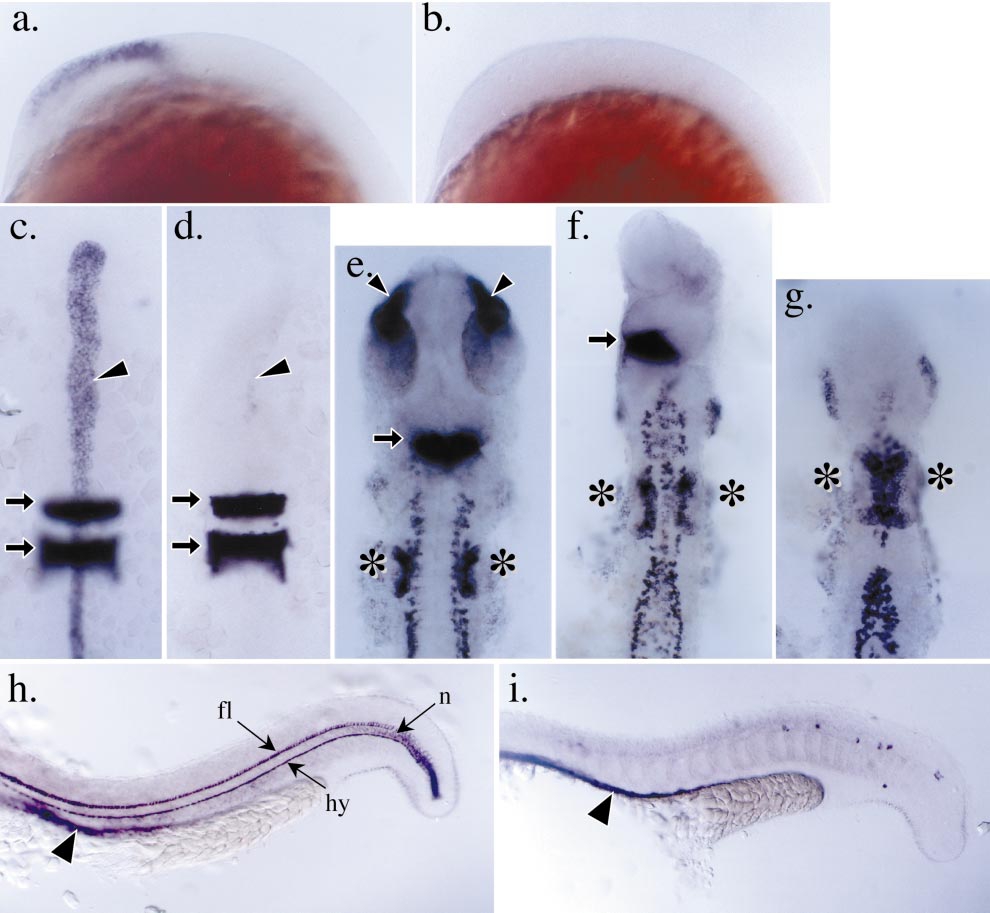
Fig. 6 Impaired anterior neural ectoderm patterning in boz mutants. (a and b) Profile views of the developing head region in postgastrula embryos (14 hpf); the expression of emx1 is detected in the developing forebrain region in wild-type embryos (a) and absent in severely affected boz mutant embryos (b). (c and d) The expression of the floorplate and notochord marker, shh, and hindbrain marker, krox20, in the anterior of wild-type and boz mutant embryos, respectively, at 12 hpf. The embryos have been removed from their yolk cell and mounted flat between coverslips. Anterior is toward the top. At this stage in wild-type embryos (c), shh expression (arrowhead) is detected in the dorsal midline and krox20 is expressed in the hindbrain region in presumptive rhombomeres 3 and 5 (arrows). In severely affected boz mutant embryos (d), the expression of shh is reduced or absent, but the development of the hindbrain indicated by the expression of krox20 appears unaffected. (e– g) Expression of paxb in wild-type and boz mutant embryos at 22 hpf. Embryos have been removed from their yolk cell and mounted flat with anterior toward the top. Embryos are aligned with the anterior extent of the pronepherous at the bottom. (e) In the anterior of wild-type embryos, paxb expression is detected in the developing eye stalks (arrowheads), the midbrain–hindbrain boundary (arrow), the otic placodes (asterisks), the neurons, and the pronepherous. (f, g) boz mutant embryos can be grouped into a series of truncations of anterior neuronal fates. For example, mildly affected boz mutants (f) exhibit a loss of eye stalk expression and a reduced midbrain–hindbrain boundary expression of paxb. In severely affected boz embryos (g), these anterior neural deficiencies are enhanced to include a loss of midbrain–hindbrain expression of paxb. Note that the otic placodes in these severely affected mutants appear to be enlarged (asterisks). (h and i) Expression of α-coll2a in the trunk and tail of wild-type and boz mutant embryos, respectively, at 22 hpf. At this stage in wild-type embryos (h), α-coll2a is detected in the floorplate (fl), notochord (n), hypochord (hy), and axial endoderm (arrowhead). In boz mutant embryos (i), the floorplate, notochord, and hypochord are reduced or absent. However, the expression of α-coll2a in the axial endoderm is still detected ventral to the dorsal midline (arrowhead).
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 215(2), Koos, D.S. and Ho, R.K., The nieuwkoid/dharma homeobox gene is essential for bmp2b repression in the zebrafish pregastrula, 190-207, Copyright (1999) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.