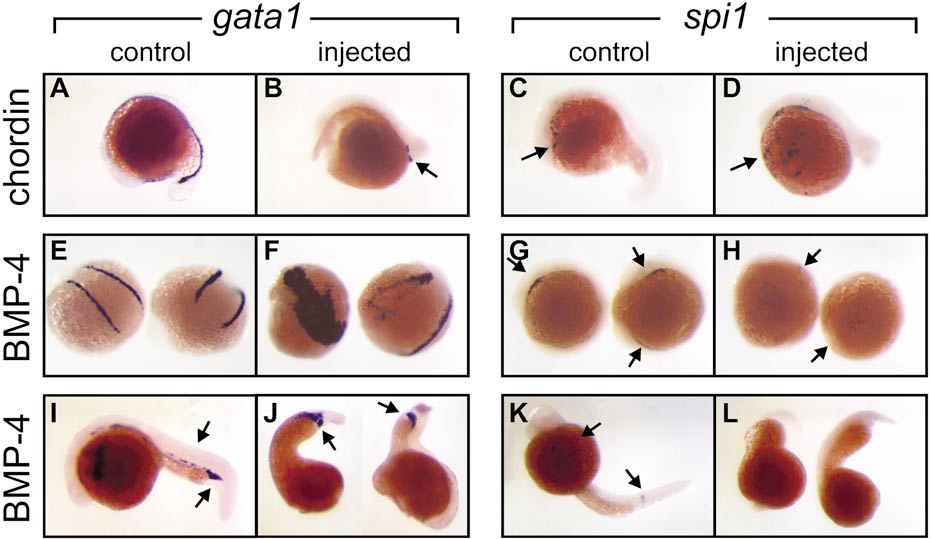
Fig. 7 Caudal erythroid commitment (marked by gata1 expression) and rostral myeloid commitment (marked by spi1 expression) can proceed independently of each other. Whole-mount in situ hybridization preparations displaying regions of gata1 and spi1 expression in embryos either untreated (control) or injected with mRNA encoding the Xenopus BMP-4 or chordin proteins as indicated to the left. (A–D) Nontreated (A, C) and chordin mRNA-injected (B, D) embryos at 18–20 hpf showing that chordin-expressing embryos have reduced gata1 expression (arrow A, B) in the caudal intermediate cell mass (ICM) but retain rostral spi1 expression in the lateral plate mesoderm (LPM) (arrow, C, D). (E–H) Nontreated (E, G) and BMP-4 mRNA-injected (F, H) embryos at 12–14 hpf showing that BMP-4-expressing embryos have reduced extent of spi1 expression (arrow, G, H) but a markedly expanded domain of gata1 expression (arrow E, F). (I–L) Nontreated (I, K) and BMP-4 mRNA-injected (J, L) embryos at 24 hpf showing BMP-4-expressing embryos have reduced extent of spi1 expression (arrow, K) but a markedly expanded domain of gata1 expression in the posterior ICM (arrow, I, J). Images are illustrative of 169 Xenopus chordin-injected (53% severe, 47% moderate-mild) and 204 BMP-4-injected (44% severe, 56% moderate-mild) and control uninjected or diluent-injected embryos, collected for analysis from several independent injection days (BMP-4, n = 11; chordin, n = 6).
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 246(2), Lieschke, G.J., Oates, A.C., Paw, B.H., Thompson, M.A., Hall, N.E., Ward, A.C., Ho, R.K., Zon, L.I., and Layton, J.E., Zebrafish SPI-1 (PU.1) marks a site of myeloid development independent of primitive erythropoiesis: implications for axial patterning, 274-295, Copyright (2002) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.