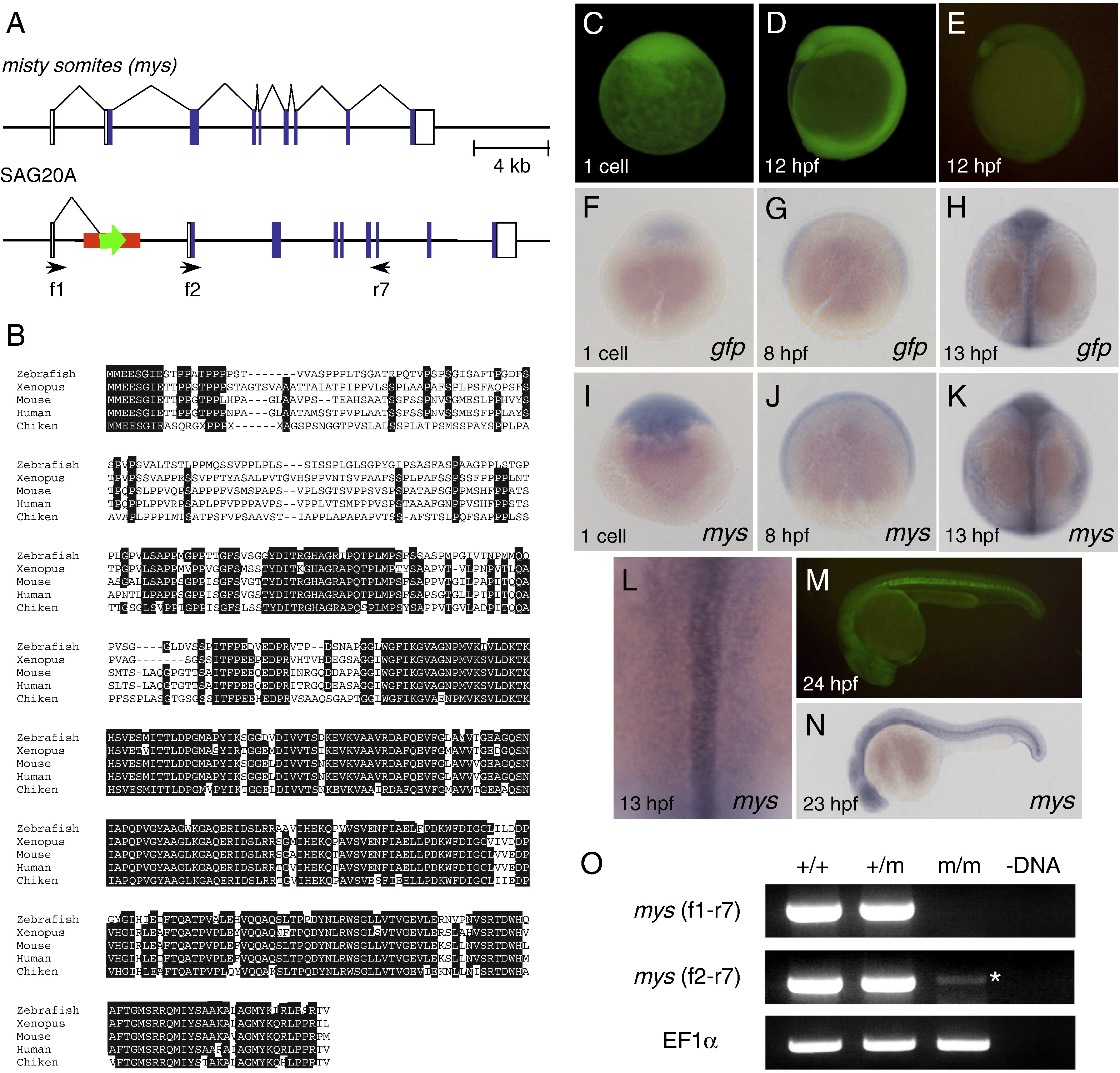
Fig. 2 Characterization of the SAG20A insertion and the mys gene. (A) The structure of the wild type misty somites (mys) locus and the SAG20A insertion. White boxes indicate untranslated regions and blue boxes indicate coding regions of the mys gene. Arrows indicate primers used for RT-PCR. (B) Comparison of the amino acid sequences of the Mys proteins in zebrafish, Xenopus, mouse, human and chicken by using ClustalW. Identical amino acids are highlighted in white. (C, D) Maternal GFP expression at the one cell stage (C) and 12 hpf (D). Embryos were obtained from a cross between an SAG20A heterozygous female and a wild type male. The absence of the SAG20A insertion in this embryo was confirmed by PCR at later stages. (E) Zygotic GFP expression at 12 hpf. Embryos were obtained from a cross between an SAG20A heterozygous male and a wild type female. (F–L) In situ hybridization using the gfp probe (F–H) and the mys probe (I–L). (F) A one-cell stage embryo obtained from a cross between an SAG20A heterozygous female and a wild type male. 8 hpf (G) and 13 hpf (H) embryos obtained from an SAG20A heterozygous male and a wild type female. One-cell stage (I), 8 hpf (J), and 13 hpf (K, L) wild type embryos. mys is expressed in the notochord and weakly and diffusely in the paraxial mesoderm at 13 hpf. (M) Zygotic GFP expression at 24 hpf. Embryos were obtained from a cross between an SAG20A heterozygous male and a wild type female. (N) In situ hybridization of a wild type embryo at 23 hpf using the mys probe. (O) RT-PCR analysis of the mys transcript. RNA was prepared from wild type (+/+), heterozygous (+/m) and homozygous embryos (m/m) at 24 hpf and used for cDNA synthesis. (-DNA) A negative control without template DNA. RT-PCR was carried out by using f1 and r7 (top), f2 and r7 (middle), and the EF1&alpha primers (bottom: positive control). An asterisk indicates a weak transcript with an aberrant start site detected in homozygous embryos.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 316(2), Kotani, T., and Kawakami, K., misty somites, a maternal effect gene identified by transposon-mediated insertional mutagenesis in zebrafish that is essential for the somite boundary maintenance, 383-396, Copyright (2008) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.