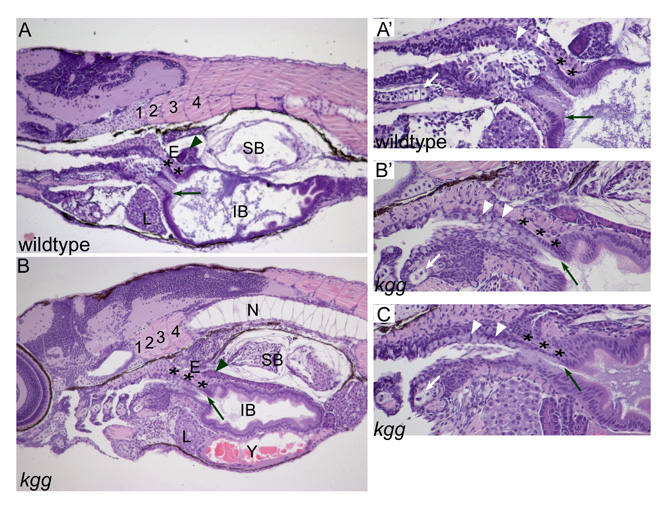
Fig. S2 kgg phenotype persists into larval stages. The esophageal-intestinal junction, indicated by the black arrow, is shifted posteriorly in kgg larvae at 7dpf. The esophageal region, indicated by asterisks, may be expanded. (A) Wild type. 100x. (A′) Specimen from A shown at 200x. Note the distinct junction between the posterior pharyngeal epithelium, indicated by white arrowheads, and the pale-staining columnar esophageal epithelium. (B) kgg mutant. 100x. The notochord is partially in the plane of section of the somites because of medial-lateral curvature. (B′) Specimen from B shown at 200x. The epithelium posterior to the fifth gill arch is ambiguous in appearance and we could not identify a pharyngeal-esophageal junction. (C) Anterior endodermal epithelium of another kgg specimen, shown at 200x. Wild type, n=4; kgg, n=6. Numbers indicate somites. E, esophagus; IB, intestinal bulb; L, liver; N, notochord; SB, swim bladder; Y, yolk; black arrow, esophageal-intestinal junction; white arrow, fifth gill arch; black arrowhead, pancreas; white arrowhead, epithelium posterior to fifth gill arch. Hematoxylin and Eosin-stained sagittal sections, anterior to left.
Image
Figure Caption
Figure Data
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Development