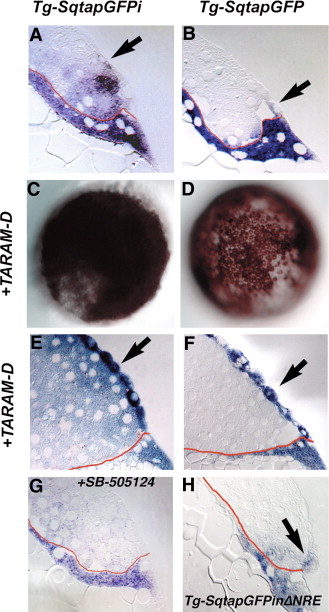
Fig. 3 Expression of gfp in the blastomeres depends on Nodal signaling. Distribution of gfp mRNA in sections of 5 hpf Tg-SqtapGFPi (A, E, G), Tg-SqtapGFP (B, F) and Tg-SqtapGFPiΔNRE (H) embryos stained to reveal gfp mRNA. Whole mounts of Tg-SqtapGFPi (C) and Tg-SqtapGFP (D) are also depicted. In all sections, the membrane that separates the YSL from the blastomeres is highlighted in red. (A) In Tg-SqtapGFPi, gfp transcripts are localized in the EVL (arrow), the blastomeres, and the YSL. (B) In Tg-SqtapGFP, gfp is expressed predominantly in the YSL and EVL (arrow). Expression is also observed in rare blastomeres adjacent to the YSL or EVL. (C, E) In response to activation of the Nodal pathway by ubiquitous expression of TARAM-D, gfp is globally expressed in Tg-SqtapGFPi embryos. In section, gfp transcripts are observed in all blastomeres, EVL cells (E, arrows), and the YSL. (D, F) In Tg-SqtapGFP embryos, TARAM-D induces gfp expression throughout the embryo (D), but only in the EVL cells (F, arrow). (G) When Nodal signaling is blocked by treatment with SB-505124 in Tg-SqtapGFPi embryos, gfp expression is reduced, but not eliminated in the YSL and EVL, and is eliminated in the blastomeres. (H) In Tg-SqtapGFPiΔNRE embryos, gfp expression is restricted to the EVL (arrow) and YSL.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 310(2), Fan, X., Hagos, E.G., Xu, B., Sias, C., Kawakami, K., Burdine, R.D., and Dougan, S.T., Nodal signals mediate interactions between the extra-embryonic and embryonic tissues in zebrafish, 363-378, Copyright (2007) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.