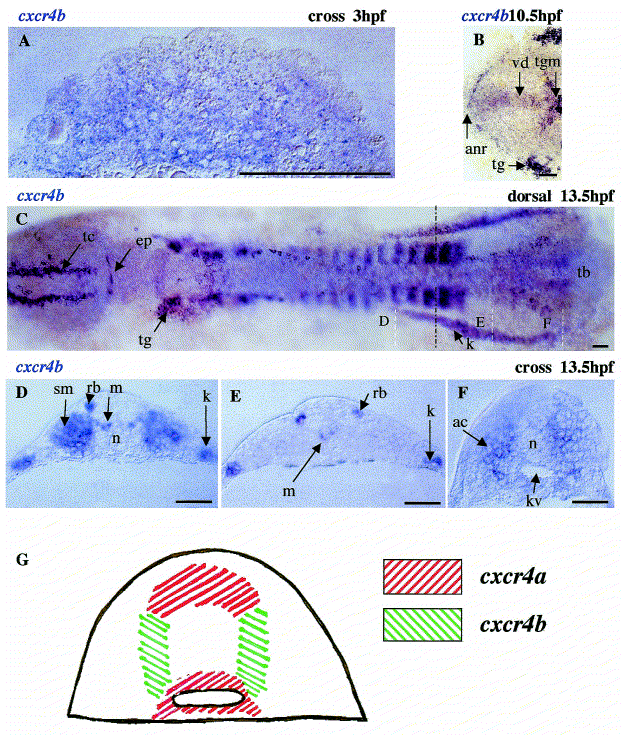
Fig. 4 Expression of cxcr4b during early zebrafish development. Expression of cxcr4b has been detected by whole-mount in situ hybridization mainly in deep cells starting from the blastula stage (A). Later on during early neurulation, the level of expression increases in specific regions of the CNS, including the posterior midbrain, the set of sensory neurons (trigeminal ganglia, dorsal sensory cells, epiphysis and telencephalon) (B,C), anterior neural ridge, ventral diencephalon and ventral midbrain (B). In addition, expression is detected in the posterior lateral mesoderm (C,F), where the level of expression increases just before formation of somites. White dashed lines in (C) indicate the level of cross-sections in reference to (D–F). The broken black line shows the border of segmented and unsegmented lateral mesoderm. The complementary mode of expression of the two genes is most obvious in the tail bud. Here, cxcr4a transcripts are in the neural plate and endodermal precursors, while cxcr4b transcripts are in mesodermal cells lateral to the notochord bud (modified from Fig. 3 and Fig. 4). This results in the bulb of the notochord being surrounded by cells specifically expressing one of the two genes (see schematic in (G)). ac, adaxial cells; anr, anterior neural ridge; ep, epiphysis; kv, Kupffer′s vesicle; k, kidney; m, motoneuron; n, notochord; rb, Rohon–Beard cells; sm, somite; tb, tail bud; tg, trigeminal ganglion; tgm, tegmentum; tc, telencephalon; vd, ventral diencephalon. Bar, 50 μm ((A), 250 μm).
Reprinted from Mechanisms of Development, 109(2), Chong, S.-W., Emelyanov, A., Gong, Z., and Korzh, V., Expression pattern of two zebrafish genes, cxcr4a and cxcr4b, 347-354, Copyright (2001) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Mech. Dev.