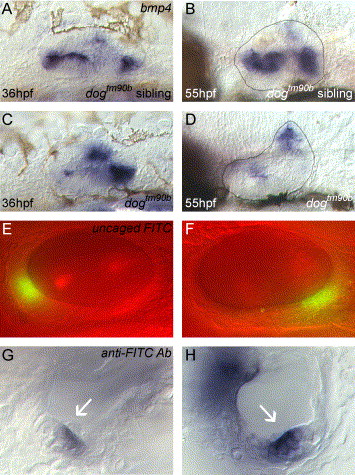
Fig. 5 Otocyst expression of bmp4 mRNA in dogtm90b and fates of cells within ventrolateral domains. (A and B) Four domains of bmp4 mRNA expression are detected in wild-type siblings at 36 (A) and 55 hpf (B) (Mowbray et al., 2001). (C and D) In dogtm90b, bmp4 mRNA expression is variably reduced in two of the ventrolateral domains and in some embryos is increased in the posterior ventrolateral domain and in the dorsal domain at 36 hpf (C). At 55 hpf, bmp4 mRNA expression in dogtm90b is virtually absent in all three ventrolateral domains, but not in the dorsal domain (D). For each of the 55 hpf embryo panels (B and D), a line has been drawn at the margin of the otic vesicle to better indicate the position of bmp4-expressing cells. (E and F) Labeling of cells by uncaging of fluorescein within anterior (E) or posterior (F) ventrolateral domains of bmp4 expression. Focal planes shown are more medial than the uncaged cells to demonstrate more clearly the location of uncaged cells relative to anterior–posterior and dorsal–ventral axes of the otocyst. The uncaged cells are more lateral than the cells in the focal plane shown. (G) Anterior ventrolateral cells labeled in E are detected in the anterior crista (white arrow) and semicircular canal at 72 hpf. (H) Posterior ventrolateral cells labeled in F are detected in the posterior crista (white arrow) and semicircular canal at 72 hpf. Embryos in A–F are shown in lateral views with anterior to the left. Embryos in G and H are shown in dorsal views with anterior to the left and medial to the top.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 277(1), Kozlowski, D.J., Whitfield, T.T., Hukriede, N.A., Lam, W.K., and Weinberg, E.S., The zebrafish dog-eared mutation disrupts eya1, a gene required for cell survival and differentiation in the inner ear and lateral line, 27-41, Copyright (2005) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.