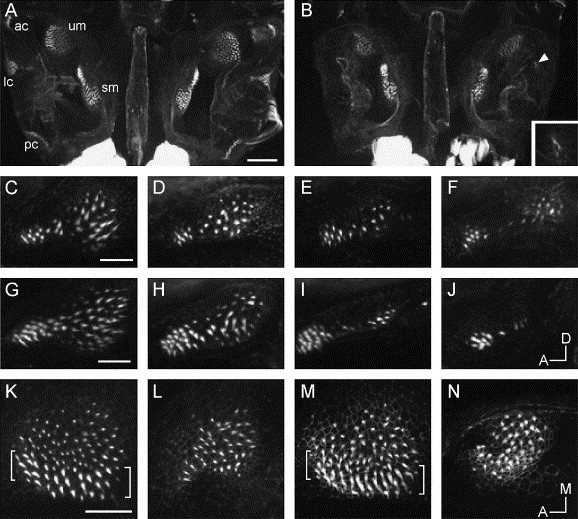
Fig. 4 Sensory patch phenotype in the ears of dog-eared homozygous embryos; confocal images of embryos and larvae stained with FITC-phalloidin. (A) Dorsal view (anterior to top) of a dissected preparation of the two ears of a 5 dpf wild-type sibling larva showing five distinct sensory patches in each ear: the utricular and saccular maculae (um, sm), and the anterior, lateral, and posterior cristae (ac, lc, pc). Scale bar, 50 μm. (B) The ears of a dogtm90b homozygote. Hair cells of the cristae are not visible in the left ear; in the right ear, three hair cells are present in the region where the lateral crista would normally form (magnified in inset). (C–J) Abnormalities in the saccular macula (orientation shown in J: anterior to left, dorsal to top): (C) lateral view of wild type, 3 dpf; (D–F) examples of saccular maculae from dogtm90b homozygous mutants, 3 dpf; (G) wild type, 5 dpf; (H–J) examples of saccular maculae from dogtm90b homozygous mutants, 5 dpf. Scale bar, 20 μm. (K–N) Abnormalities in the utricular macula (orientation shown in N: anterior to left, medial to top): (K and M) dorsal views of utricular maculae from phenotypically wild-type siblings, 5.5 dpf; (L) dogtm90b homozygote, 5.5 dpf; (N) dogtp85b homozygote, 5.5 dpf. Brackets to the left and right of the wild-type maculae shown in K and M indicate the hair cells with long stereociliary bundles located at the lateral edges of the maculae; this type of hair cell is mostly absent in the maculae of dog embryos (L and N). Scale bar, 20 μm.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 277(1), Kozlowski, D.J., Whitfield, T.T., Hukriede, N.A., Lam, W.K., and Weinberg, E.S., The zebrafish dog-eared mutation disrupts eya1, a gene required for cell survival and differentiation in the inner ear and lateral line, 27-41, Copyright (2005) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.