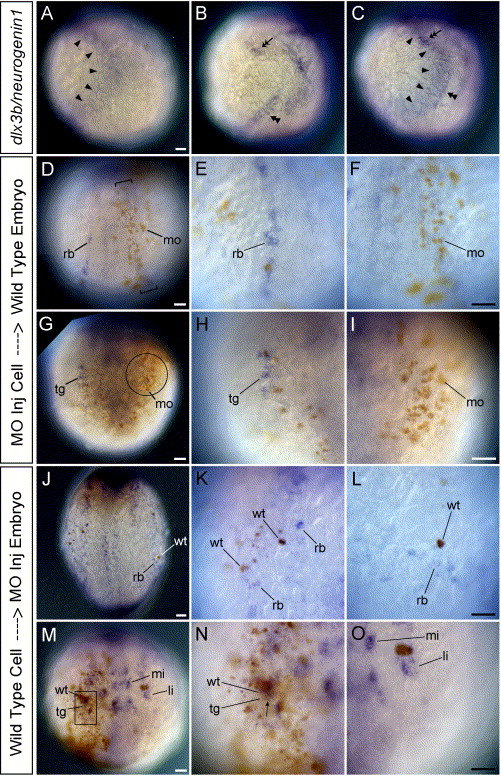
Fig. 9 HuC expression in mosaic embryos between wild-type and MOs-injected embryos. (A–C) Wild-type embryos at tailbud stage. Lateral views, and dorsal is to the right. (D–O) Transplanted embryos at 3-somite stage. D–I are the wild-type host embryos. (J–O) are the MOs-injected host embryos. (D and J) Dorsal views. (G and M) Anterior views. (A) Expression pattern of dlx3b (arrowheads). (B) Expression pattern of neurogenin1 (double arrowhead in the trunk and double arrow in the head). (C) Expression pattern of dlx3b and neurogenin1. (D–O) HuC expression in mosaic embryos. (A–C) show that dlx3b expression (arrowheads) and neurogenin1 expression in the lateral trunk (double arrowhead) are adjoining but not overlapping in the trunk. In contrast, dlx3b expression and neurogenin1 expression in the lateral head (double arrow) are overlapping. D–F show that RB neurons (rb) do not develop in the neural plate where brown-labeled MOs-injected cells (mo) are in a narrow region (bracket) just outside the neural plate. dlx3b and dlx4b should be expressed in this narrow region under wild-type conditions. (E) A high magnification view of RB neurons (rb) on the left side of embryo in D. (F) A high magnification view of the narrow region defined by brackets on the right side of embryo in D. The high number of MO-injected cells (brown, mo) is able to inhibit HuC expression in neighboring cells. G–I show that neurons in the trigeminal placodes (tg) do not develop there when brown-labeled MOs-injected cells occupy the trigeminal placode (circle). dlx3b and dlx4b are expressed in this circle region under wild-type conditions. (H) A high magnification view of neurons in the trigeminal placode (tg) on the right side of embryo in G. (I) A high magnification view of the trigeminal placodal region defined by the circle on the left side of embryo in G. The high number of MO injected cells (brown, mo) is able to inhibit HuC expression in the trigeminal placode. (J–L) In a MO-injected background, RB neurons are seen only around the brown-labeled wild-type cells (wt) in the embryonic epidermis. The host MOs-injected embryos develop no or reduced levels of RB neurons. (K) A high magnification view of RB neurons on the left side of embryo in J. RB neurons can be seen only around the brown wild-type cells (wt). (L) A high magnification view of RB neurons on the right side of embryo in J. RB neurons can be seen only around the brown wild-type cells (wt). (M–O) Neurons in the trigeminal placodes develop when brown-labeled wild-type cells occupy the trigeminal placode (square) in the host MOs-injected embryos having no trigeminal placodal neurons. N is the high magnification view of the trigeminal placode defined by the square on the right side of embryo in M. The high number of wild-type cells expresses HuC in themselves, so many double-labeled neurons can be seen in the trigeminal placode (arrow). (O) A high magnification view of the trigeminal placodal region on the left side of embryo in M. No neurons in the trigeminal placode are observed where wild-type cells are not present. li, anterior lateral hindbrain interneuron; mi, anterior medial hindbrain interneuron. All scale bars, 50 μm. Scale bar in A applies for A, B, and C. Scale bar in F applies for both E and F, etc.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 276(2), Kaji, T., and Artinger, K.B., dlx3b and dlx4b function in the development of Rohon-Beard sensory neurons and trigeminal placode in the zebrafish neurula, 523-540, Copyright (2004) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.