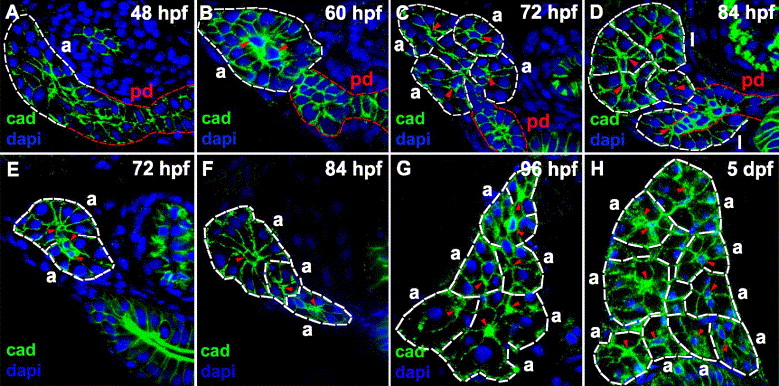
Fig. 6 Acinar gland morphogenesis during larval development. (A–D) Histological sections through the anterior pancreas (rostral to islet) of larvae processed for cadherin (green) immunohistochemistry and dapi (blue). The main pancreatic duct and the acini are demarcated (red and white dashed lines respectively), and centroacinar cells are indicated (red arrowheads). (A) At 48 hpf, the distal end of the main pancreatic duct appears as a multi-layered stratified epithelium (white dashed lines). (B) By 60 hpf, a primitive acinus-like structure is formed. (C) At 72 hpf, four distinct acini are recognized. (D) By 84 hpf, two exocrine lobules are evident. (E–H) Histological cross-sections through the pancreas (caudal to islet) of larvae processed for cadherin immunohistochemistry (green) and dapi (blue). Acini (demarcated by white dashed lines) are shown. Acinar number increases on successive days post-fertilization. Two, three, six and nine acini are identified in these 72 hpf (E), 84 hpf (F), 96 hpf (G) and 5 dpf (120 hpf) (H) larvae, respectively. pd: pancreatic duct; a: acinus; l: exocrine lobule; cad: cadherin.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 284(1), Yee, N.S., Lorent, K., and Pack, M., Exocrine pancreas development in zebrafish, 84-101, Copyright (2005) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.