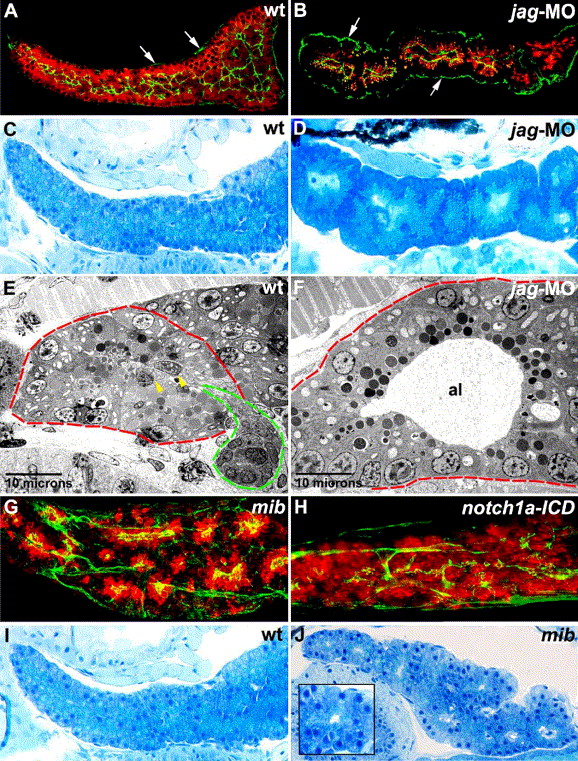
Fig. 10 Notch signaling regulates pancreatic duct development. (A, B) Sagittal optical section (A) and histological section (B) of the pancreas of wild type (A) and jagged2/3 morpholino-injected (B) 5 dpf larvae processed for cpa (red) and cyk (green) immunohistochemistry (IHC), right lateral view. Cpa is present in the jagged morpholino-injected larva (B), although the levels are reduced compared with wild type (A). By contrast, the ductal system is markedly reduced in the jagged morpholino-injected larva (B). (C, D) Sagittal histological sections through the pancreas of 5 dpf wild type (C) and jagged morpholino-injected (D) larvae. Note the contiguous enlarged acini present in the jagged morpholino-injected larva. By contrast, individual wild type acini are difficult to delineate because they are numerous, relatively small and in close proximity to each other. (E, F) Transmission electron micrographs showing acini (red dashed lines) from wild type (E) and jagged morpholino-injected (F) larvae. The acinar lumen of the jagged morpholino-injected larva is dilated, and centroacinar cells are absent. An intercalated duct exiting the wild type acinus is evident (green dashed line), and two centroacinar cells are indicated by yellow arrowheads. (G, H) Confocal projection of larvae processed for cyk (green) and cpa (red) IHC. Cyk IHC shows altered ductal morphology in mib (G) and Notch-activated (H) larvae. Cpa IHC shows clusters of enlarged acini in mib (G), whereas following Notch activation, the level and distribution of cpa protein are near normal (H), compared with wild type pancreas (Figs. 4O and P; Figs. 9A5 and A6). (I, J) Sagittal histological sections through the 5 dpf wild type (I) and mib (J) pancreas, right lateral view. Note enlarged acini (inset showing a magnified view) in the mib larva. jag-MO: jagged2/3 morphant; mib: mind bomb; notch1a-ICD: notch1a-intracellular domain; cpa: carboxypeptidase A; cyk: cytokeratin; al: acinar lumen. Arrows in panels (A) and (B) point to immunoreactive cyk in pancreatic connective tissue.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 284(1), Yee, N.S., Lorent, K., and Pack, M., Exocrine pancreas development in zebrafish, 84-101, Copyright (2005) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.