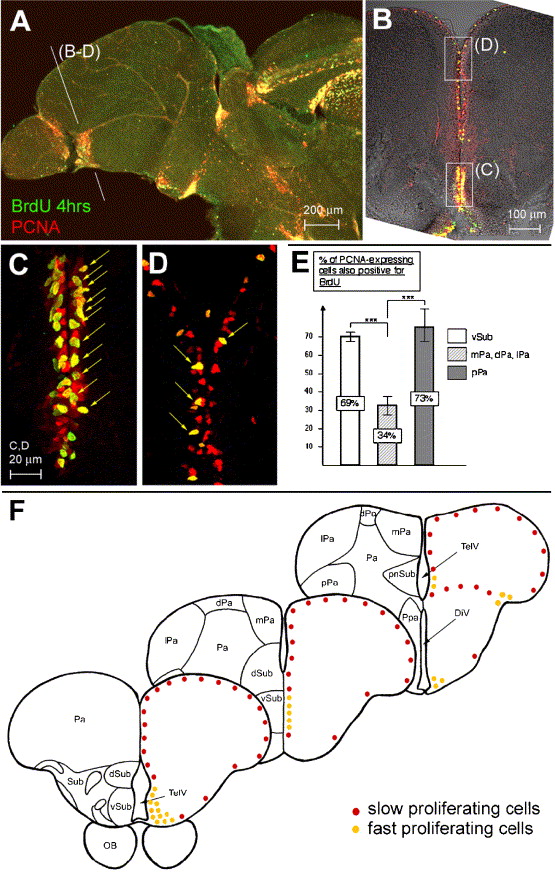
Fig. 2 Different cell cycle characteristics between proliferation zones in the adult zebrafish telencephalon. (A–D) Double immunolabeling for PCNA (red) and BrdU (green) on sagital (A, anterior left) and cross (panels B–D, dorsal up) vibratome sections observed under confocal microscopy; panels C, D are the areas boxed in panel B observed at higher magnification and on an optic section of 1.5 μm. PCNA expression and BrdU-positive cells are concentrated ventrally (compare the density of PCNA-only (red) and double-labeled (yellow arrows) cells in B–D). (E) Labeling index (number of PCNA-positive cells that are also BrdU-positive) in the telencephalon along the DV axis. In the anterior telencephalon: 69% in the ventral subpallium, n = 115 PCNA-positive cells counted, against 33.7% in the dorsal subpallium, medial, dorsal, and lateral pallium, n = 327; at the surface of the posterior pallium: 73%, n = 26. (F) Schematic representation of the zones of fast (yellow dots) and slow (red dots) proliferation in the zebrafish adult telencephalon, as identified in panels A–E. Cross-sections are oriented along the AP axis. Abbreviations: see Fig. 1, and DiV: diencephalic ventricle, dPa: dorsal pallium, dSub: dorsal subpallium, lPa: lateral pallium, mPa: medial pallium, pnSub: postcommisural nucleus of the ventral subpallium, Ppa: preoptic nucleus, pPa: posterior pallium, TelV: telencephalic ventricle, vSub: ventral subpallium.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 295(1), Adolf, B., Chapouton, P., Lam, C.S., Topp, S., Tannhauser, B., Strähle, U., Gotz, M., and Bally-Cuif, L., Conserved and acquired features of adult neurogenesis in the zebrafish telencephalon, 278-293, Copyright (2006) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.