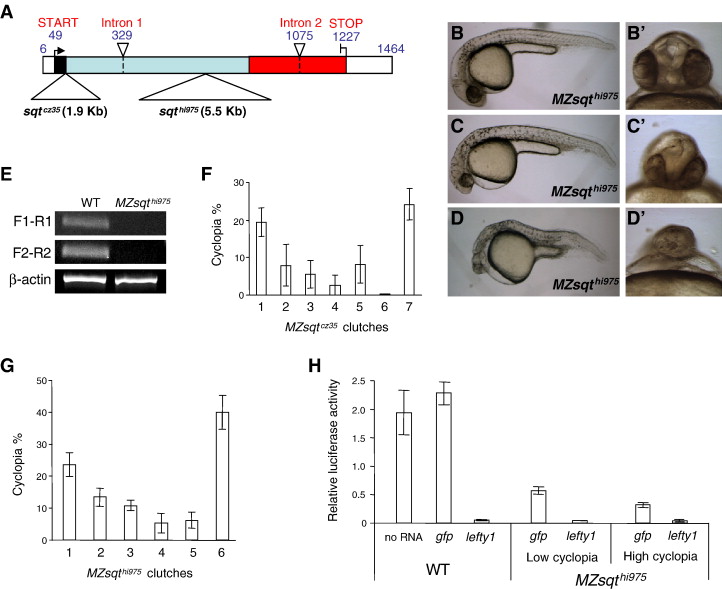
Fig. 1 Genetic background influences sqt penetrance. (A) Schematic diagram of sqtcz35 and sqthi975 alleles. The following features of sqt's three exons are indicated: 5′ and 3′ UTR (white boxes); signal sequence (black box); pro-domain (light blue box) and mature ligand domain (red box). Points of the sqtcz35 1.9 Kb and the sqthi975 5.5 Kb insertions (large triangles) and introns (small triangles, dashed lines) are indicated. (B–D) Phenotypic range of MZsqthi975/hi95embryos. Lateral views of normal (B), mildly affected (C) and strongly affected (D) MZsqthi975/hi975 embryos. Apostrophes (′) indicate a frontal view of the same specimen. (E) RT-PCR analysis of sqt mRNA in MZsqthi975/hi975embryos. cDNA extracted from WT and MZsqthi975/hi975 embryos at the 8-cell stage were used as template to analyze maternal sqt mRNA levels. F1-R1 shows the amplicon obtained from F1 and R1 primer pair, spanning the mRNA coordinates 3 to 165. F2-R2 shows the amplicon obtained from F2 and R2 primer pair, spanning the mRNA coordinates 962–1180. β-actin was used as an internal reference for the RT-PCR. Both amplicons are reduced or absent in MZsqthi975/hi975 embryos. (F–G) Genetic background determines sqt penetrance. For both MZsqtcz35/cz35 (F) and MZsqthi975/hi975 (G) embryos, incidences of cyclopia were scored on the second day of development (30–36 hpf). Reproducible cyclopia penetrance rates were observed over repeat crosses of the same parental pairs, whereas distinct penetrance rates were often obtained from different crosses. Each bar represents the average cyclopia penetrance of several hundred (197 < n < 774) embryos from three (MZsqtcz35/cz35) or four (MZsqthi975/hi975) repeat crosses, with standard deviations indicated. See Table S1 for details. (H) Residual Nodal activity is inversely correlated with cyclopia penetrance. WT embryos, as well as low-cyclopia (2%, n = 112) and high-cyclopia (24%, n = 107) MZsqthi975/hi975 embryos were used to measure the Nodal activity by ARE-reporter assay. 25 pg of luciferase reporter plasmids, plus 30 pg of either gap43-gfp or lefty1 mRNA were injected into each group of embryos. WT embryos without mRNA injection (labeled as “no RNA”) were used to establish standard Nodal activity levels. WT embryos injected with lefty1 mRNA were used to establish the baseline activity of the reporter system in the absence of Nodal activity. Average values and standard deviations of triplicate experiments are shown.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 308(2), Pei, W., Williams, P.H., Clark, M.D., Stemple, D.L., and Feldman, B., Environmental and genetic modifiers of squint penetrance during zebrafish embryogenesis, 368-378, Copyright (2007) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.