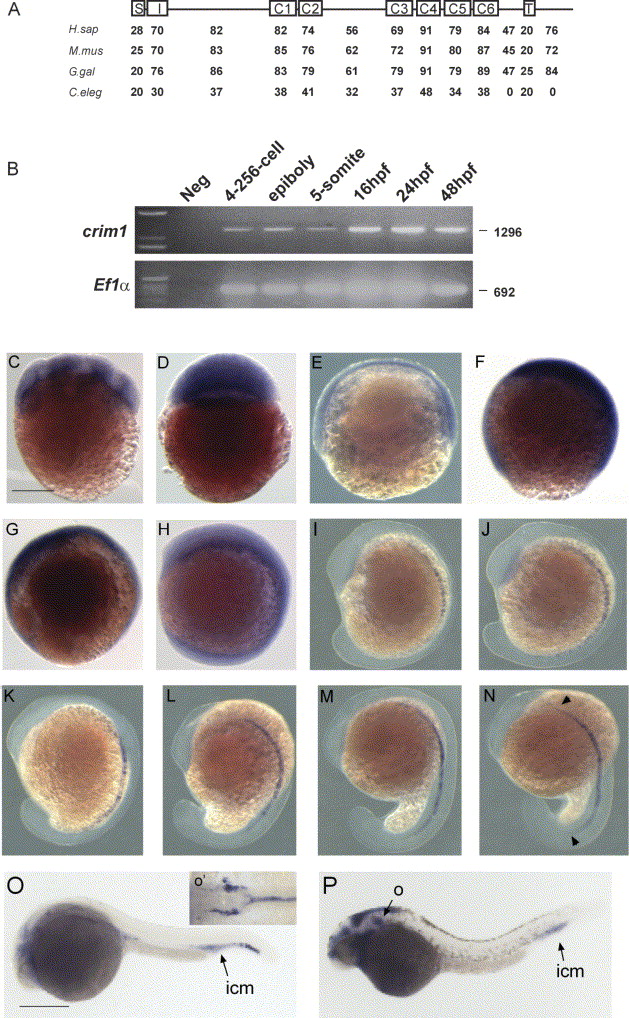
Fig. 1 Cloning and expression of zebrafish crim1. (A) Ideogram of the zebrafish Crim1 protein, showing domain homology (%) to human (H. sap), mouse (M. mus) and chicken (G. gal) Crim1 orthologs and C. elegans B0024.14 (C. eleg) proteins. S, signal peptide; I, insulin-like growth factor binding protein like domain; C1-6, Von Willebrand factor C type repeats; T, transmembrane domain; (B) crim1 positive signal was observed at non-saturation PCR conditions at all stages examined from blastula (256-1K cell) to 48 hpf. cDNA specific primers amplifying the ubiquitously expressed elongation factor-1 alpha (EF1α) was used as a loading control (Nordnes et al., 1994). (C-P) Expression of crim1 (C-P) at 16-cell (C), sphere (D), 50% epiboly (E), 75% epiboly (F), 90% epiboly (G), six-somite (H), 10-somite stage (I), 14-somite (J), 16-somite (K), 18-somite (L), 20-somite (M), 21 hpf (N), 24 hpf (O) and 30 hpf (P). All embryos are shown laterally with anterior to the top. In N, arrows denote anterior and posterior limits of crim1 expression in the notochord; in O and P, ICM; intermediate cell mass; O, otic vesicle; note the expanded ICM denoted by the arrow in B (severe panel). Inset in O (O′) is a dorsal view with anterior to the left of the embryo in O and represents the dorsal aorta (DA) and posterior cardinal vein (PCV). We note that the expression of crim1 in the brain ventricle (P) may be due to trapping of the riboprobe. Scale bar in C-N=250 μm; O and P=500 μm.
Reprinted from Mechanisms of Development, 123(4), Kinna, G., Kolle, G., Carter, A., Key, B., Lieschke, G.J., Perkins, A., and Little, M.H., Knockdown of zebrafish crim1 results in a bent tail phenotype with defects in somite and vascular development, 277-287, Copyright (2006) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Mech. Dev.