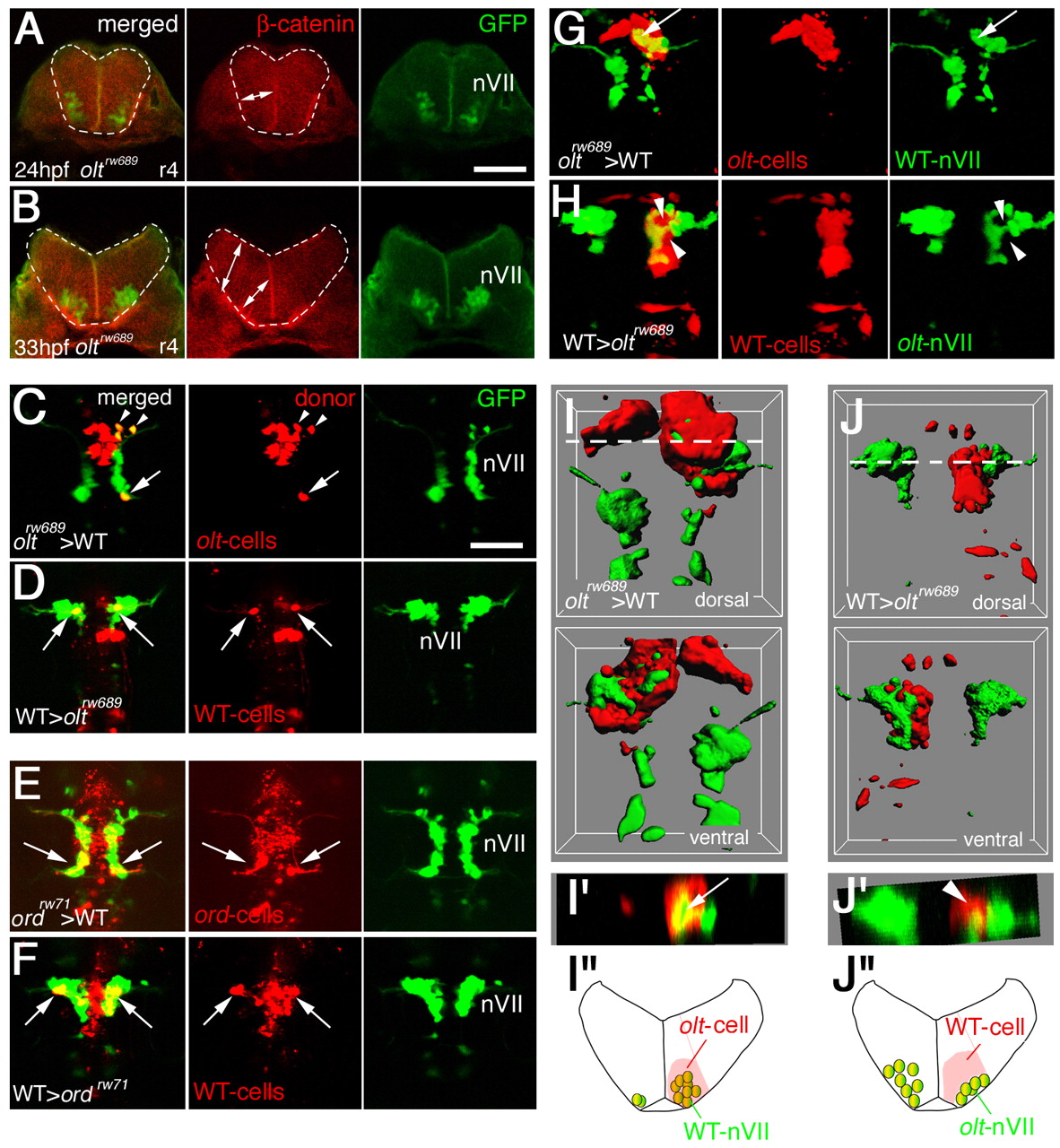
Fig. 6 Functional fz3a and celsr2 genes in neuroepithelial cells are required for preventing integration of nVII motor neurons into the neuroepithelium. (A,B) Single focal-plane images of cross sections at r4 in olt Isl1-GFP embryos stained with anti-β-catenin antibody (red) at 24 (A) and 33 (B) hpf. Orientation of the neuroepithelial cells is shown by double-headed arrows. Hindbrain regions are outlined by broken lines. (C-F) Mosaic experiments were performed to determine the cell autonomy of the olt and ord genes. The donor cells were labeled with rhodamine-conjugated dextran (red). The nVII motor neurons (arrows) derived from the oltrw689 (C) and ordrw71 (E) Isl1-GFP embryos migrated caudally in the wild-type host embryos, although some were still located in r4 at the time of observation (arrowheads in C). By contrast, none of the wild-type-derived nVII motor neurons (arrows) reached r6 in the olt (D) and ord (F) host embryos. Red puncta signals may be the debris of the dead transplanted cells. However, as we observed the growth of the peripheral axons of the nVII motor neurons in each mosaic embryo (see Materials and methods), it is unlikely that such debris had serious adverse effects on the development of these embryos. Dorsal views of the embryos are shown. (G-J) Embryos showing mosaicism in the neuroepithelium at the r4 region. When the olt-derived cells were incorporated into the neuroepithelium of the wild-type host embryos at r4, the nVII motor neurons migrated aberrantly into the mutant neuroepithelium (arrows in G and I'). By contrast, when wild-type-derived cells were incorporated into the r4 region of the olt host embryos, the nVII motor neurons failed to invade the wild-type neuroepithelium (arrowheads in H and J'). (C-H) Images are composite stacks of serial optical sections. (I,J) Computationally reconstructed 3D images of the embryos shown in G and H. Dorsal and ventral views of the embryos are shown. In I, mismigrated nVII motor neurons (green) are hidden by the surrounding olt embryo-derived neuroepithelial cells (red) as no transparency was given to the images of the donor-cell clusters. (I',J') Computationally reconstructed cross sections at r4 indicated by the broken line in I and J. (I',J'') Schematic cross sections at r4 of the embryos shown in G and H, respectively. The yellow signals in the merged panels of G and H are technical artifacts caused by the superimposition of the red signals of the donor cells and the green signals of the motor neurons. As red signals were not detected in the axons of the motor neurons (G,H, middle panels), all of the nVII motor neurons were derived from the host embryos. Scale bars: 50 μm in A for A,B; and 50 μm in C for C-H.
Image
Figure Caption
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Development