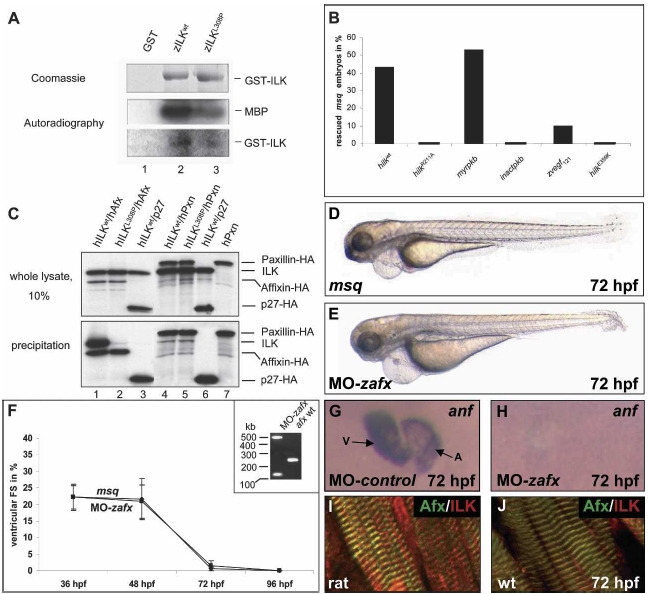
Fig. 5 msq mutant ILKL308P disrupts ILK kinase activity and its binding to β-parvin (Affixin). (A) In comparison to zILKwt, the msq mutation zILKL308P leads to potent reduction of phosphorylation of the substrate MBP (middle part), as well as of ILK autophosphorylation (lower part). (Upper part) Identical amounts of purified recombinant zILKwt (lane 2) and zILKL308P (lane 3) were used. Lane 1 shows incubation of MBP with GST as a control. (B) Rescue of the msq mutant heart phenotype by mRNA injection of various constructs. Kinase-deficient hilk (hilk R211A), as well as hilk deficient in β-parvin binding (hilk E359K) fail to rescue the msq mutant phenotype, whereas wild-type hilk wt is able to rescue the msq phenotype. Injection of either zvegf121 mRNA, or myristoylated human PKB (myrpkb) mRNA suppresses the msq mutant phenotype. Injection of kinase inactive hPKB (inactpkb) mRNA has no effect. (C, lower panel) In vitro coimmunoprecipitation with human β-parvin, Paxillin, and ILK. HA-tagged hβ-parvin (hAfx) interacts with wild-type hILKwt (lane 1), but not with mutant hILKL308P (lane 2). In contrast, HA-tagged hPaxillin (hPxn) precipitates with both hILKwt (lane 4) and hILKL308P (lane 5). (Lanes 3,6) As a control, HA-tagged hp27Kip1 is used. Lane 7 indicates precipi-tation of HA-tagged hPaxillin to exclude degradation products of hPaxillin migrating at the size of hILK. The upper panel shows 10% input of the radiolabeled, cotranslated proteins. (D–H) Antisense oligonucleotide-mediated knockdown of zebrafish β-parvin (affixin) phenocopies the msq mutant heart phenotype. MO-zafx injected embryos (E) are indistinguishable from msq mutant embryos (D) and display severe impairment of ventricular contractility. (F) Similar to msq mutant embryos, fractional shortening (FS) of the ventricular chamber decreases significantly in MO-zafx-injected embryos. The effect of MO-zafx on mRNA splicing is shown in the inset. Injection of MO-zafx results in abnormal splice products of 500 bp (integration of intron 5) and 125 bp (skipping of exon 5), both predicted to lead to premature termination of translation of zilk. (G,H) In contrast to wild-type hearts (G), zanf RNA cannot be detected by RNA antisense in situ hybridization in hearts from MO-zafx injected embryos at 72 hpf (H). Atrium (A) and ventricle (V) are indicated. (I,J) β-Parvin (Afx) and ILK colocalize at sarcomeric Z-discs of zebrafish (J) and rat hearts (I).
Image
Figure Caption
Figure Data
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Genes & Dev.