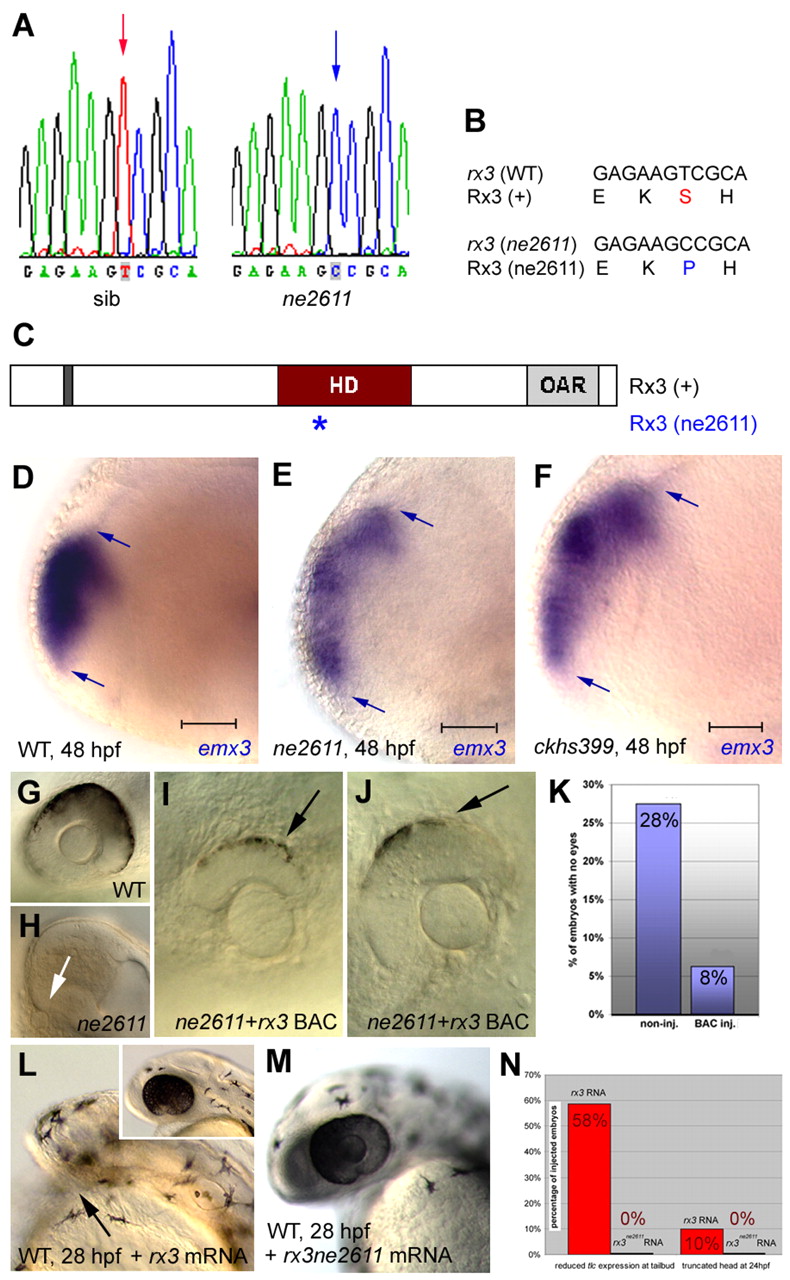
Fig. 3 ne2611 is a new null allele of rx3. (A) Sequencing trace data of rx3 cDNA from a ne2611 mutant (right) and a wild-type sibling (left) reveals a T to C transition (arrows). (B,C) Rx3 protein sequences (B) and structures (C) in wild type (+) and ne2611 mutants. The ne2611 mutation leads to a Serine to Proline exchange within the Rx3 homeodomain (asterisk in C). Dark gray box, octapeptide; red box, homeodomain; light gray box, otparistaless-rx domain. (D-F) Expression of the telencephalic marker emx3 in wild-type (D), ne2611 (E) and ckhs399 (F) embryos at 48 hpf (lateral views, anterior left; scale bar: 0.02 mm). ckhs399 embryos display a telencephalic expansion similar to that of ne2611 mutants. (G-K) Embryos from a ne2611/+ ne2611/+ cross were injected at the one-cell stage with BAC CHORB736A01233Q containing the rx3 locus and are observed at 24 hpf. (I,J) Representative injected ne2611 mutants; note the restoration of the retina compared with uninjected wild type (G) or ne2611 (H; small lens in H indicated by the white arrow). (K) Percentage of embryos lacking eyes after BAC injection compared with non-injected embryos. BAC injection restored retinal development in 79% of mutant embryos. (L,M) Phenotypes triggered by ectopic expression of wild-type rx3 versus rx3ne2611 mRNA. Wild-type embryos were injected at the one-cell stage and observed at 24 hpf (lateral views, anterior left). Ectopic expression of rx3 causes head truncations (L, arrow; compare with wild type, inset) whereas rx3ne2611 has no effect (M). (N) Percentage of embryos showing reduction of tlc expression (left two bars) (see Fig. S2 in the supplementary material) or head truncation (right two bars) following injection of rx3 or rx3ne2611 mRNA (as indicated).
Image
Figure Caption
Figure Data
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Development