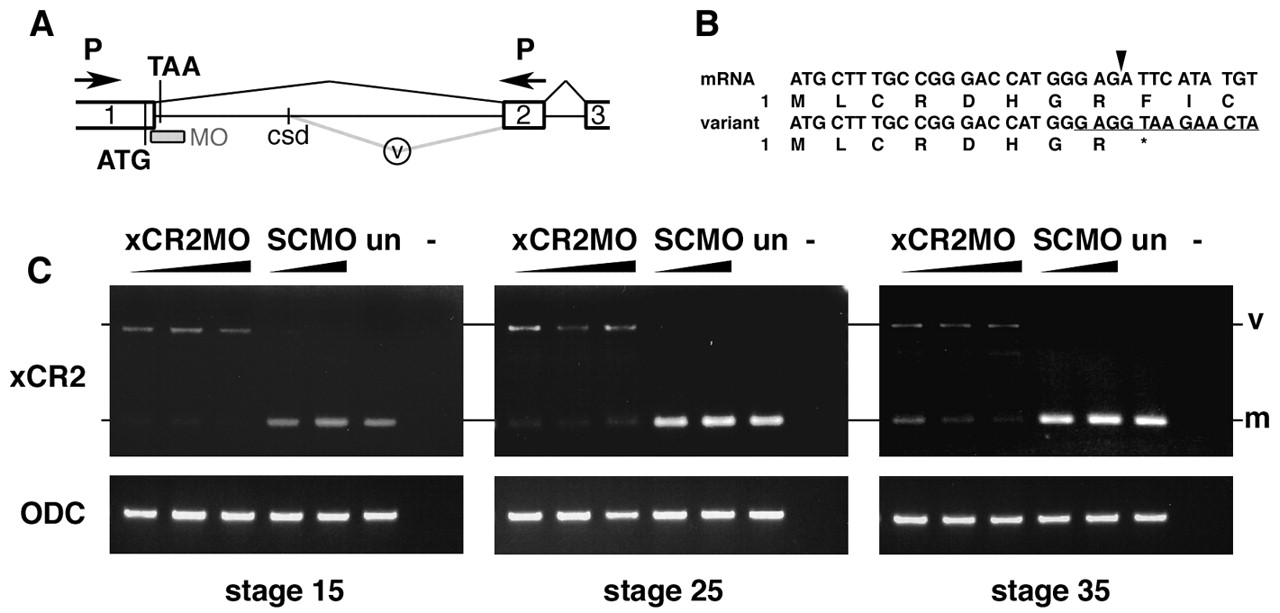
Fig. 4 XCR2 MO blocks endogenous RNA splicing. (A) Genomic structure including exon I (1), exon II (2), and exon III (3) of XCR2. The translation initiation codon (ATG) and a potential termination codon (TAA) are indicated. The splice-site-targeted antisense morpholino oligonucleotide XCR2 MO (MO) was designed against the sequence at the boundary of exon I/intron I. Abnormal splicing detected in XCR2 MO-injected embryos is shown by the gray line (v). The spliced variant is generated by a cryptic splice donor (csd) site 642 bp downstream from the end of exon I. (B) Sequence comparison of cDNA from mature mRNA and the aberrant splicing variant. Amino acid sequences are also indicated. The variant generated by abnormal splicing has a termination codon (correspondent to TAA in Fig. 4A) right after the end of exon I. Arrowhead indicates the correct exon I/exon II splice junction. The target sequence of XCR2 MO is underlined. (C) RT-PCR analyses of XCR2 mRNA in XCR2 MO-injected embryos. Embryos were injected with 10, 20 and 50 ng of XCR2 MO, or 20 and 50 ng of Standard Control MO (SC MO), and harvested for RT-PCR at stage 15, 25 and 35. The primer set was designed to span the first intron to detect splicing of the endogenous XCR2 pre-mRNA. In XCR2 MO-injected embryos, the mature mRNA (m) was decreased and an abnormal splicing variant (v) was detected. At stage 35, the mature XCR2 mRNA was detectable at low levels in embryos injected with lowest dose (10 ng) of XCR2 MO.
Image
Figure Caption
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ BMC Genomics