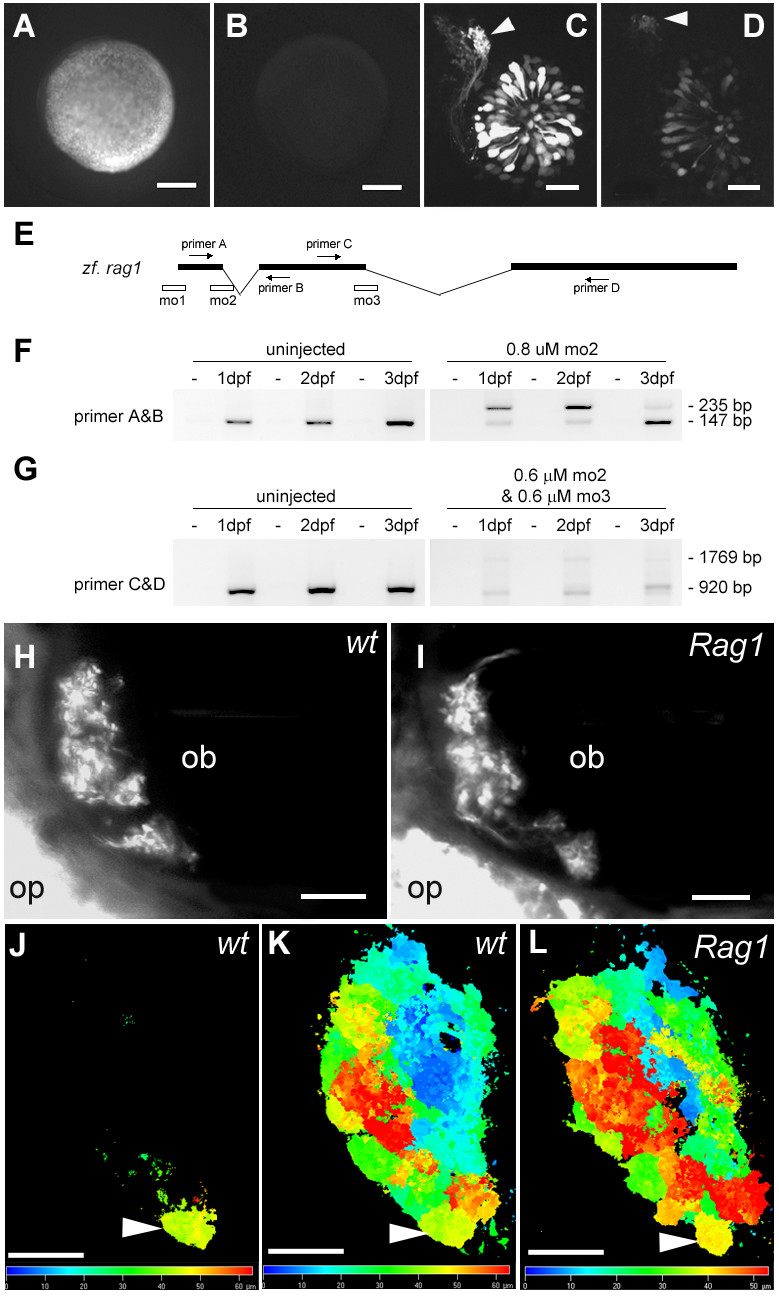
Fig. 5 The effect of RAG1 depletion on the olfactory projection. (A) An embryo injected with mRNA encoding the 5' end of Rag1 fused to EGFP. (B) An embryo co-injected with the Rag1-EGFP fusion mRNA and mo1. (C) Olfactory neurons labelled with GFP under the Rag1 promoter, with brightly labeled axons projecting to a single target (arrowhead), at 3 dpf. (D) In a transgenic embryo injected with mo1, axons still project to the same target (arrowhead), but the intensity of GFP fluorescence is reduced. (E) A schematic diagram of the Rag1 gene, showing the location of morpholinos and primers that were used to analyse morpholino-injected fish. (F) RT-PCR on control or mo2 injected embryos. Abnormal splicing occurs in the morpholino-injected fish, leading to a premature stop codon, as indicated by sequencing of the upper band. (G) RT-PCR after injection of a mixture of Rag1 mo2 and mo3, showing loss of the normal transcript. (H, I) A subset of Di8ANEPPQ-labeled olfactory sensory neurons in 7-day old wild type and Rag1 mutant fish. Axons innervate all target structures detectable in this optical plane in the mutant. (J-L) SV2-labelled 4 day-old Rag1:GFP transgenic (J, K) and Rag1 mutant (L) forebrains, shown in dorsal view. The images are colour-coded according to depth. The glomerulus innervated by the strong GFP-positive neurons (J) is indicated by the arrowhead. Bar = 100 µm (A, B); 20 µm (C, D, H-K). The colour bars in J and K indicate depth. Embryos in panels H-L are shown in dorsal view, with anterior to the left.
Image
Figure Caption
Figure Data
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ BMC Neurosci.