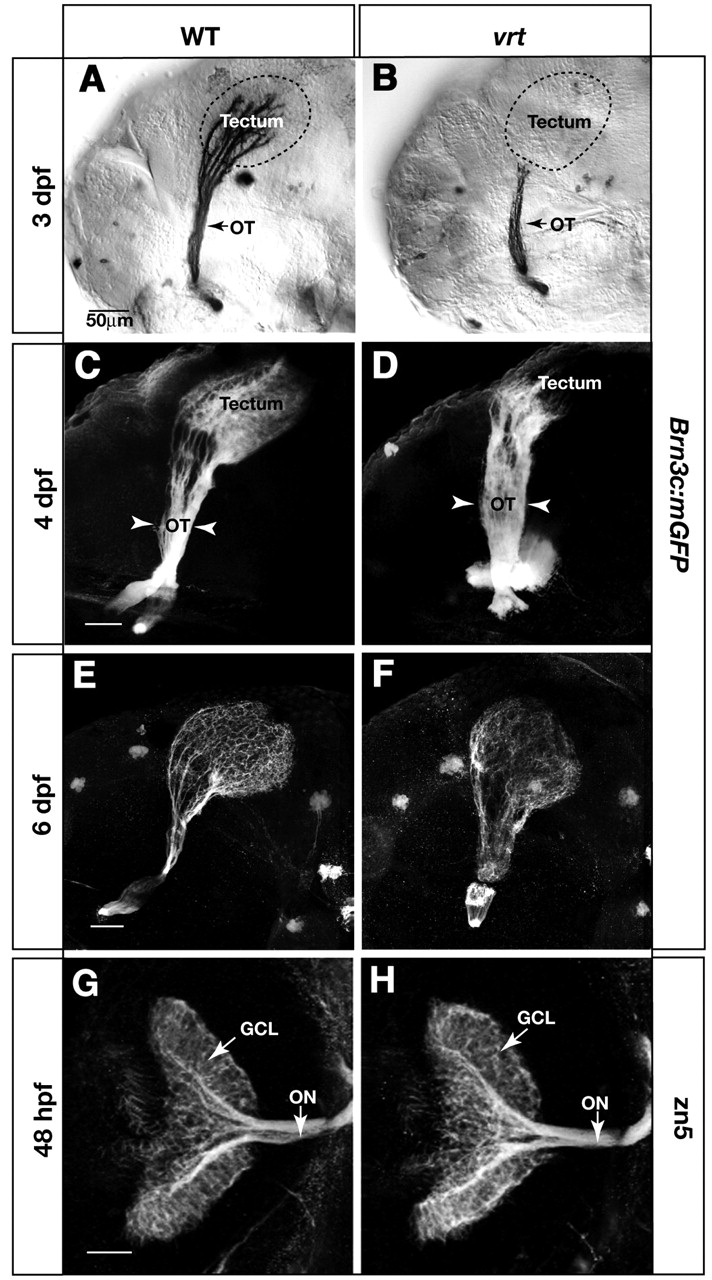
Fig. 4 vertigo (vrt) mutants show severely delayed innervation of the tectum. Analysis of retinal axon projection in wild type (A,C,E,G) and vrt mutants (B,D,F,H). (A-F) Lateral views of the retinotectal projection in Brn3c:mGFP transgenic fish, labeled with anti-GFP. At 3 dpf, the wild-type tectum (A) is fully innervated, while the vrt tectum (B) is devoid of axons. Broken lines outline the tectum boundaries. In 4 dpf wild-type larvae (C), the density of axon arbors is increased compared with 3 dpf (A), and dorsal and ventral branches are clearly visible in the optic tract. In vrt (D), axons have invaded the anterior tectum, and the optic tract (OT) is abnormally wide (arrowheads). At 6 dpf, axons innervate the whole tectum in the vrt mutant (F) similar to wild type (E) The optic tract remains wider than normal. (G,H) Dorsal views of 48 hpf retinas and optic nerves, labeled with zn5. The number of RGCs and their axons is similar between wild type (G) and vrt (H). Scale bars: 50 µm.